Toll-like receptors in antiviral innate immunity
- PMID: 24316048
- PMCID: PMC3943763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.11.024
Toll-like receptors in antiviral innate immunity
Abstract
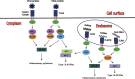
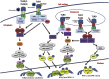
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are fundamental sensor molecules of the host innate immune system, which detect conserved molecular signatures of a wide range of microbial pathogens and initiate innate immune responses via distinct signaling pathways. Various TLRs are implicated in the early interplay of host cells with invading viruses, which regulates viral replication and/or host responses, ultimately impacting on viral pathogenesis. To survive the host innate defense mechanisms, many viruses have developed strategies to evade or counteract signaling through the TLR pathways, creating an advantageous environment for their propagation. Here we review the current knowledge of the roles TLRs play in antiviral innate immune responses, discuss examples of TLR-mediated viral recognition, and describe strategies used by viruses to antagonize the host antiviral innate immune responses.
Keywords: cytokine; interferon; interferon regulatory factor; nuclear factor-kappa B; virus.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. Toll-like receptor and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1143:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity. 2011;34:637–650. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R., Janeway C.A. Decoding the patterns of self and nonself by the innate immune system. Science. 2002;296:298–300. - PubMed
-
- Palsson-McDermott E.M., O'Neill L.A. Building an immune system from nine domains. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35:1437–1444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

