Increased de novo lipogenesis is a distinct characteristic of individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 24316260
- PMCID: PMC6276362
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.11.049
Increased de novo lipogenesis is a distinct characteristic of individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Background & aims: There have been few studies of the role of de novo lipogenesis in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). We used isotope analyses to compare de novo lipogenesis and fatty acid flux between subjects with NAFLD and those without, matched for metabolic factors (controls).
Methods: We studied subjects with metabolic syndrome and/or levels of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase >30 mU/L, using magnetic resonance spectroscopy to identify those with high levels (HighLF, n = 13) or low levels (LowLF, n = 11) of liver fat. Clinical and demographic information was collected from all participants, and insulin sensitivity was measured using the insulin-modified intravenous glucose tolerance test. Stable isotopes were administered and gas chromatography with mass spectrometry was used to analyze free (nonesterified) fatty acid (FFA) and triacylglycerol flux and lipogenesis.
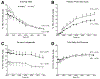
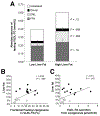
Results: Subjects with HighLF (18.4% ± 3.6%) had higher plasma levels of FFAs during the nighttime and higher concentrations of insulin than subjects with LowLF (3.1% ± 2.7%; P = .04 and P < .001, respectively). No differences were observed between groups in adipose flux of FFAs (414 ± 195 μmol/min for HighLF vs 358 ± 105 μmol/min for LowLF; P = .41) or production of very-low-density lipoprotein triacylglycerol from FFAs (4.06 ± 2.57 μmol/min vs 4.34 ± 1.82 μmol/min; P = .77). In contrast, subjects with HighLF had more than 3-fold higher rates of de novo fatty acid synthesis than subjects with LowLF (2.57 ± 1.53 μmol/min vs 0.78 ± 0.42 μmol/min; P = .001). As a percentage of triacylglycerol palmitate, de novo lipogenesis was 2-fold higher in subjects with HighLF (23.2% ± 7.9% vs 10.1% ± 6.7%; P < .001); this level was independently associated with the level of intrahepatic triacylglycerol (r = 0.53; P = .007).
Conclusions: By administering isotopes to subjects with NAFLD and control subjects, we confirmed that those with NAFLD have increased synthesis of fatty acids. Subjects with NAFLD also had higher nocturnal plasma levels of FFAs and did not suppress the contribution from de novo lipogenesis on fasting. These findings indicate that lipogenesis might be a therapeutic target for NAFLD.
Keywords: Diabetes; Fatty Acid Kinetics; Lipid Metabolism; Obesity.
Copyright © 2014 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors had any conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 2004;40:1387–1395. - PubMed
-
- Charlton MR, Burns JM, Pedersen RA, et al. Frequency and outcomes of liver transplantation for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in the United States. Gastroenterology 2011;141:1249–1253. - PubMed
-
- Iozzo P, Turpeinen AK, Takala T, et al. Defective liver disposal of free fatty acids in patients with impaired glucose tolerance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89:3496–502. - PubMed
-
- Sanyal AJ, Campbell-Sargent C, Mirshahi F, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: association of insulin resistance and mitochondrial abnormalities. Gastroenterology 2001;120:1183–1192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

