Comparison of the effect of naproxen, etodolac and diclofenac on postoperative sequels following third molar surgery: a randomised, double-blind, crossover study
- PMID: 24316711
- PMCID: PMC4015047
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.19518
Comparison of the effect of naproxen, etodolac and diclofenac on postoperative sequels following third molar surgery: a randomised, double-blind, crossover study
Abstract
Objective: To compare the three non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs) Diclofenac potassium, Etodolac and Naproxen sodium in relation to pain, swelling and trismus following impacted third molar surgery.
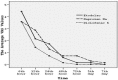
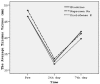
Study design: The study was a randomized and a double-blinded study which included 42 healthy young individuals with impacted third molars and bone retention. Patients were randomly assigned to 3 groups (n: 14) to which Diclofenac potassium, Naproxen sodium and Etodolac were administered orally an hour before the operation. Impacted third molars were surgically extracted with local anaesthesia. Visual analog scales (VAS) were used to assess the pain in the 6th, 12th hours and on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 5th, and 7th days postoperatively. Swelling was evaluated using ultrasound (US) and mouth opening (trismus) was measured with a composing stick pre and post operatively on the 2nd and 7th days respectively.
Results: Regarding pain alleviation, Diclofenac potassium was better than Naproxen sodium and Naproxen sodium was better than Etodolac but these differences were not statistically significant. US measurements showed that the swelling on postoperative 2nd day was significantly lowest with Diclofenac potassium as compared to others (p= 0.027) while Naproxen sodium and Etodolac acted similarly (p=0.747). No difference was noted regarding trismus in any of the groups.
Conclusion: NSAIDs (Diclofenac, Naproxen and Etodolac) are somehow similarly effective for controlling pain and trismus following extraction of mandibular third molars but Diclofenac potassium surpasses others in reduction of swelling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Blondeau F, Daniel NG. Extraction of impacted mandibular third molars: postoperative complications and their risk factors. J Can Dent Assoc. 2007;73:325. - PubMed
-
- Morrison BW, Fricke J, Brown J, Yuan W, Kotey P, Mehlisch D. The optimal analgesic dose of rofecoxib: overview of six randomized controlled trials. J Am Dent Assoc. 2000;131:1729–37. - PubMed
-
- Barden J, Edwards JE, McQuay HJ, Wiffen PJ, Moore RA. Relative efficacy of oral analgesics after third molar extraction. Br Dent J. 2004;197:407–11. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y, Rodriguez C, Dionne RA. The role of COX-2 in acute pain and the use of selective COX-2 inhibitors for acute pain relief. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11:1737–55. - PubMed
-
- Bjørnsson GA, Haanaes HR, Skoglund LA. Naproxen 500 mg bid versus acetaminophen 1000 mg qid: effect on swelling and other acute postoperative events after bilateral third molar surgery. J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;43:849–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

