A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation
- PMID: 24316715
- PMCID: PMC3911877
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1432
A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation
Abstract
N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is the most prevalent and reversible internal modification in mammalian messenger and noncoding RNAs. We report here that human methyltransferase-like 14 (METTL14) catalyzes m(6)A RNA methylation. Together with METTL3, the only previously known m(6)A methyltransferase, these two proteins form a stable heterodimer core complex of METTL3-METTL14 that functions in cellular m(6)A deposition on mammalian nuclear RNAs. WTAP, a mammalian splicing factor, can interact with this complex and affect this methylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

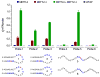
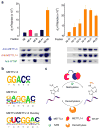
References
-
- Bokar JA. The biosynthesis and functional roles of methylated nucleosides in eukaryotic mRNA. In: Grosjean H, editor. Fine-Tuning of RNA Functions by Modification and Editing. Vol. 12. Springer-Verlag; Berlin Heidelberg: 2005. pp. 141–177.
-
- Motorin Y, Helm M. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011;2:611–631. - PubMed
-
- Beemon K, Keith J. J Mol Biol. 1977;113:165–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

