Ecology and genetic structure of zoonotic Anisakis spp. from adriatic commercial fish species
- PMID: 24317085
- PMCID: PMC3911056
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03561-13
Ecology and genetic structure of zoonotic Anisakis spp. from adriatic commercial fish species
Abstract
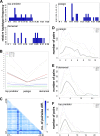
Consumption of raw or thermally inadequately treated fishery products represents a public health risk, with the possibility of propagation of live Anisakis larvae, the causative agent of the zoonotic disease anisakidosis, or anisakiasis. We investigated the population dynamics of Anisakis spp. in commercially important fish-anchovies (Anisakis), sardines (Sardina pilchardus), European hake (Merluccius merluccius), whiting (Merlangius merlangus), chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus), and Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus)-captured in the main Adriatic Sea fishing ground. We observed a significant difference in the numbers of parasite larvae (1 to 32) in individual hosts and between species, with most fish showing high or very high Anisakis population indices. Phylogenetic analysis confirmed that commercial fish in the Adriatic Sea are parasitized by Anisakis pegreffii (95.95%) and Anisakis simplex sensu stricto (4.05%). The genetic structure of A. pegreffii in demersal, pelagic, and top predator hosts was unstructured, and the highest frequency of haplotype sharing (n = 10) was between demersal and pelagic fish.
Figures


References
-
- European Food Safety Authority 2010. Scientific opinion of the Panel on Biological Hazards on risk assessment of parasites in fishery products. EFSA J. 8:10–43. 10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1543 - DOI
-
- Marcogliese DJ. 1995. The role of zooplankton in the transmission of helminth parasites to fish. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 5:336–371. 10.1007/BF00043006 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

