A new in vitro anti-tumor polypeptide isolated from Arca inflata
- PMID: 24317469
- PMCID: PMC3877886
- DOI: 10.3390/md11124773
A new in vitro anti-tumor polypeptide isolated from Arca inflata
Abstract
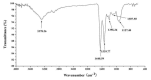
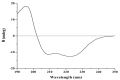
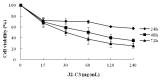
A new in vitro anti-tumor polypeptide, coded as J2-C3, was isolated from Arca inflata Reeve and purified by diethyl-aminoethanol (DEAE)-sepharose Fast Flow anion exchange and phenyl sepharose CL-4B hydrophobic chromatography. J2-C3 was identified to be a homogeneous compound by native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Native-PAGE). The purity of J2-C3 was over 99% in reversed phase-high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC). The molecular weight was determined as 20,538.0 Da by electrospray-ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS). J2-C3 was rich in Glx (Gln + Glu), Lys, and Asx (Asp + Asn) according to amino acid analysis. Four partial amino acid sequences of this peptide were determined as L/ISMEDVEESR, KNGMHSI/LDVNHDGR, AMKI/LI/LNPKKGI/LVPR and AMGAHKPPKGNEL/IGHR via MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS and de novo sequencing. Secondary structural analysis by CD spectroscopy revealed that J2-C3 had the α-helix (45.2%), β-sheet (2.9%), β-turn (26.0%) and random coil (25.9%). The anti-tumor effect of J2-C3 against human tumor cells was measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, and the IC₅₀ values of J2-C3 were 65.57, 93.33 and 122.95 µg/mL against A549, HT-29 and HepG2 cell lines, respectively. Therefore, J2-C3 might be developed as a potential anti-tumor agent.
Figures





References
-
- Singh R., Sharma M., Joshi P., Rawat D.S. Clinical status of anti-cancer agents derived from marine sources. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2008;8:603–617. - PubMed
-
- Suárez Y., González L., Cuadrado A., Berciano M., Lafarga M., Muñoz A. Kahalalide F, a new marine-derived compound, induces oncosis in human prostate and breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2003;2:863–872. - PubMed
-
- Riely G.J., Gadgeel S., Rothman I., Saidman B., Sabbath K., Feit K., Kris M.G., Rizvi N.A. A phase 2 study of TZT-1027, administered weekly to patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Lung Cancer. 2007;55:181–185. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.10.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

