Determinants of mortality in a combined cohort of 501 patients with HIV-associated Cryptococcal meningitis: implications for improving outcomes
- PMID: 24319084
- PMCID: PMC3922213
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cit794
Determinants of mortality in a combined cohort of 501 patients with HIV-associated Cryptococcal meningitis: implications for improving outcomes
Abstract
Background: Cryptococcal meningitis (CM) is a leading cause of death in individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Identifying factors associated with mortality informs strategies to improve outcomes.
Methods: Five hundred one patients with HIV-associated CM were followed prospectively for 10 weeks during trials in Thailand, Uganda, Malawi, and South Africa. South African patients (n = 266) were followed for 1 year. Similar inclusion/exclusion criteria were applied at all sites. Logistic regression identified baseline variables independently associated with mortality.
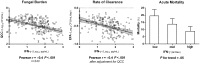
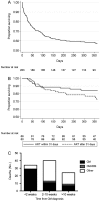
Results: Mortality was 17% at 2 weeks and 34% at 10 weeks. Altered mental status (odds ratio [OR], 3.1; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.7-5.9), high cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) fungal burden (OR, 1.4 per log10 colony-forming units/mL increase; 95% CI, 1.0-1.8), older age (>50 years; OR, 3.9; 95% CI, 1.4-11.1), high peripheral white blood cell count (>10 × 10(9) cells/L; OR, 8.7; 95% CI, 2.5-30.2), fluconazole-based induction treatment, and slow clearance of CSF infection were independently associated with 2-week mortality. Low body weight, anemia (hemoglobin <7.5 g/dL), and low CSF opening pressure were independently associated with mortality at 10 weeks in addition to altered mental status, high fungal burden, high peripheral white cell count, and older age. In those followed for 1 year, overall mortality was 41%. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome occurred in 13% of patients and was associated with 2-week CSF fungal burden (P = .007), but not with time to initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART).
Conclusions: CSF fungal burden, altered mental status, and rate of clearance of infection predict acute mortality in HIV-associated CM. The results suggest that earlier diagnosis, more rapidly fungicidal amphotericin-based regimens, and prompt immune reconstitution with ART are priorities for improving outcomes.
Keywords: Cryptococcus neoformans; HIV; antiretroviral therapy; cryptococcal meningitis; mortality (determinants).
Figures
References
-
- Hakim JG, Gangaidzo IT, Heyderman RS, et al. Impact of HIV infection on meningitis in Harare, Zimbabwe: a prospective study of 406 predominantly adult patients. AIDS. 2000;14:1401–7. - PubMed
-
- Bekondi C, Bernede C, Passone N, et al. Primary and opportunistic pathogens associated with meningitis in adults in Bangui, Central African Republic, in relation to human immunodeficiency virus serostatus. Int J Infect Dis. 2006;10:387–95. - PubMed
-
- Bicanic T, Wood R, Meintjes G, et al. High-dose amphotericin B with flucytosine for the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis in HIV-infected patients: a randomized trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:123–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

