Alterations in white matter structure in young children with type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 24319123
- PMCID: PMC3898758
- DOI: 10.2337/dc13-1388
Alterations in white matter structure in young children with type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether type 1 diabetes affects white matter (WM) structure in a large sample of young children.
Research design and methods: Children (ages 4 to <10 years) with type 1 diabetes (n = 127) and age-matched nondiabetic control subjects (n = 67) had diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging scans in this multisite neuroimaging study. Participants with type 1 diabetes were assessed for HbA1c history and lifetime adverse events, and glucose levels were monitored using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) device and standardized measures of cognition.
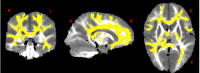
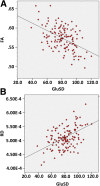
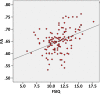
Results: Between-group analysis showed that children with type 1 diabetes had significantly reduced axial diffusivity (AD) in widespread brain regions compared with control subjects. Within the type 1 diabetes group, earlier onset of diabetes was associated with increased radial diffusivity (RD) and longer duration was associated with reduced AD, reduced RD, and increased fractional anisotropy (FA). In addition, HbA1c values were significantly negatively associated with FA values and were positively associated with RD values in widespread brain regions. Significant associations of AD, RD, and FA were found for CGM measures of hyperglycemia and glucose variability but not for hypoglycemia. Finally, we observed a significant association between WM structure and cognitive ability in children with type 1 diabetes but not in control subjects.
Conclusions: These results suggest vulnerability of the developing brain in young children to effects of type 1 diabetes associated with chronic hyperglycemia and glucose variability.
Figures
References
-
- Mauras N, Beck R, Xing D, et al. Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study Group A randomized clinical trial to assess the efficacy and safety of real-time continuous glucose monitoring in the management of type 1 diabetes in young children aged 4 to <10 years. Diabetes Care 2012;35:204–210 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang C, DeVisser A, Martinez JA, et al. Differential impact of diabetes and hypertension in the brain: adverse effects in white matter. Neurobiol Dis 2011;42:446–458 - PubMed
-
- Malone JI, Hanna SK, Saporta S. Hyperglycemic brain injury in the rat. Brain Res 2006;1076:9–15 - PubMed
-
- Malone JI, Hanna S, Saporta S, et al. Hyperglycemia not hypoglycemia alters neuronal dendrites and impairs spatial memory. Pediatr Diabetes 2008;9:531–539 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 HD041906/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD41918/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD41906-10/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD41908-10/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD41915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD056526/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD41890/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD041890/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041915/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041908/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD078463/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD56526/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041918/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD41890-10/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD041890/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

