Human RECQ5 helicase promotes repair of DNA double-strand breaks by synthesis-dependent strand annealing
- PMID: 24319145
- PMCID: PMC3936725
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1263
Human RECQ5 helicase promotes repair of DNA double-strand breaks by synthesis-dependent strand annealing
Abstract
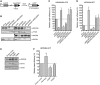
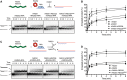
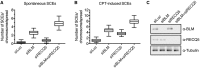
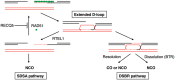
Most mitotic homologous recombination (HR) events proceed via a synthesis-dependent strand annealing mechanism to avoid crossing over, which may give rise to chromosomal rearrangements and loss of heterozygosity. The molecular mechanisms controlling HR sub-pathway choice are poorly understood. Here, we show that human RECQ5, a DNA helicase that can disrupt RAD51 nucleoprotein filaments, promotes formation of non-crossover products during DNA double-strand break-induced HR and counteracts the inhibitory effect of RAD51 on RAD52-mediated DNA annealing in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, we demonstrate that RECQ5 deficiency is associated with an increased occupancy of RAD51 at a double-strand break site, and it also causes an elevation of sister chromatid exchanges on inactivation of the Holliday junction dissolution pathway or on induction of a high load of DNA damage in the cell. Collectively, our findings suggest that RECQ5 acts during the post-synaptic phase of synthesis-dependent strand annealing to prevent formation of aberrant RAD51 filaments on the extended invading strand, thus limiting its channeling into potentially hazardous crossover pathway of HR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Physical interaction of RECQ5 helicase with RAD51 facilitates its anti-recombinase activity.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 21;285(21):15739-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.110478. Epub 2010 Mar 25. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20348101 Free PMC article.
-
Rad51 protein controls Rad52-mediated DNA annealing.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 23;283(21):14883-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801097200. Epub 2008 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18337252 Free PMC article.
-
Rad52 Restrains Resection at DNA Double-Strand Break Ends in Yeast.Mol Cell. 2019 Dec 5;76(5):699-711.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.08.017. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31542296 Free PMC article.
-
Pathways and assays for DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2019 Sep 6;51(9):879-889. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmz076. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2019. PMID: 31294447 Review.
-
RecQ helicases queuing with Srs2 to disrupt Rad51 filaments and suppress recombination.Genes Dev. 2007 Dec 1;21(23):3019-26. doi: 10.1101/gad.1624707. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 18056418 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Increased levels of RECQ5 shift DNA repair from canonical to alternative pathways.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Oct 12;46(18):9496-9509. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky727. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30107528 Free PMC article.
-
Differential and Concordant Roles for Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 and Poly(ADP-Ribose) in Regulating WRN and RECQL5 Activities.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Dec;35(23):3974-89. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00427-15. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26391948 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Lethal Interactions of RECQ Helicases.Trends Cancer. 2021 Feb;7(2):146-161. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.09.001. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Trends Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33041245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of recombination and genomic maintenance.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Aug 3;7(8):a016501. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016501. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 26238353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Recql5 mutant facilitates complex CRISPR/Cas9-mediated chromosomal engineering in mouse zygotes.Genetics. 2024 Jun 5;227(2):iyae054. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae054. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 38577877 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

