Translational approach to behavioral learning: lessons from cerebellar plasticity
- PMID: 24319600
- PMCID: PMC3844268
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/853654
Translational approach to behavioral learning: lessons from cerebellar plasticity
Abstract
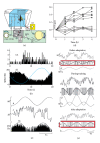
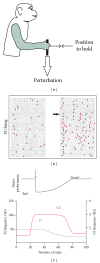
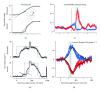
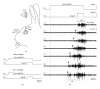
The role of cerebellar plasticity has been increasingly recognized in learning. The privileged relationship between the cerebellum and the inferior olive offers an ideal circuit for attempting to integrate the numerous evidences of neuronal plasticity into a translational perspective. The high learning capacity of the Purkinje cells specifically controlled by the climbing fiber represents a major element within the feed-forward and feedback loops of the cerebellar cortex. Reciprocally connected with the basal ganglia and multimodal cerebral domains, this cerebellar network may realize fundamental functions in a wide range of behaviors. This review will outline the current understanding of three main experimental paradigms largely used for revealing cerebellar functions in behavioral learning: (1) the vestibuloocular reflex and smooth pursuit control, (2) the eyeblink conditioning, and (3) the sensory envelope plasticity. For each of these experimental conditions, we have critically revisited the chain of causalities linking together neural circuits, neural signals, and plasticity mechanisms, giving preference to behaving or alert animal physiology. Namely, recent experimental approaches mixing neural units and local field potentials recordings have demonstrated a spike timing dependent plasticity by which the cerebellum remains at a strategic crossroad for deciphering fundamental and translational mechanisms from cellular to network levels.
Figures

References
-
- Delgado-García JM, Gruart A. The role of interpositus nucleus in eyelid conditioned responses. Cerebellum. 2002;1(4):289–308. - PubMed
-
- Delgado-García JM, Gruart A. Building new motor responses: eyelid conditioning revisited. Trends in Neurosciences. 2006;29(6):330–338. - PubMed
-
- Medina JF, Nores WL, Mauk MD. Inhibition of climbing fibres is a signal for the extinction of conditioned eyelid responses. Nature. 2002;416(6878):330–333. - PubMed
-
- Hikosaka O, Nakamura K, Sakai K, Nakahara H. Central mechanisms of motor skill learning. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 2002;12(2):217–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

