Monte Carlo and analytical model predictions of leakage neutron exposures from passively scattered proton therapy
- PMID: 24320500
- PMCID: PMC3843753
- DOI: 10.1118/1.4829512
Monte Carlo and analytical model predictions of leakage neutron exposures from passively scattered proton therapy
Abstract
Purpose: Stray neutron radiation is of concern after radiation therapy, especially in children, because of the high risk it might carry for secondary cancers. Several previous studies predicted the stray neutron exposure from proton therapy, mostly using Monte Carlo simulations. Promising attempts to develop analytical models have also been reported, but these were limited to only a few proton beam energies. The purpose of this study was to develop an analytical model to predict leakage neutron equivalent dose from passively scattered proton beams in the 100-250-MeV interval.
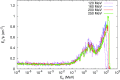
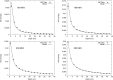
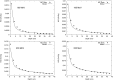
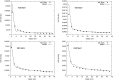
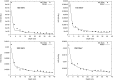
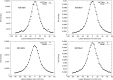
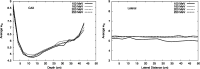
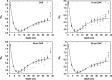
Methods: To develop and validate the analytical model, the authors used values of equivalent dose per therapeutic absorbed dose (H∕D) predicted with Monte Carlo simulations. The authors also characterized the behavior of the mean neutron radiation-weighting factor, wR, as a function of depth in a water phantom and distance from the beam central axis.
Results: The simulated and analytical predictions agreed well. On average, the percentage difference between the analytical model and the Monte Carlo simulations was 10% for the energies and positions studied. The authors found that wR was highest at the shallowest depth and decreased with depth until around 10 cm, where it started to increase slowly with depth. This was consistent among all energies.
Conclusion: Simple analytical methods are promising alternatives to complex and slow Monte Carlo simulations to predict H∕D values. The authors' results also provide improved understanding of the behavior of wR which strongly depends on depth, but is nearly independent of lateral distance from the beam central axis.
Figures
References
-
- Inskip P. D., Ries L. A. G., Cohen R. J., and Curtis R. E., “Chapter 18: New maligancies following childhood cancer,” New Malignancies Among Cancer Survivors: SEER Cancer Registries, 1973–2000 (National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD, 2006).
-
- Fraumeni J. F., Curtis R. E., Edwards A. C., and Tucker M. A., “Chapter 1: Introduction,” New Malignancies Among Cancer Survivors: SEER Cancer Registries, 1973–2000 (National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD, 2006).
-
- The International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements, “Prescribing, recording, and reporting proton-beam therapy,” ICRU Report No. 78 (ICRU Publications, Bethesda, MD, 2007).
-
- Newhauser W. D., Fontenot J. D., Mahajan A., Kornguth D., Stovall M., Zheng Y., Taddei P. J., Mirkovic D., Mohan R., Cox J. D., and Woo S., “The risk of developing a second cancer after receiving craniospinal proton irradiation,” Phys. Med. Biol. 54, 2277–2291 (2009). 10.1088/0031-9155/54/8/002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hecksel D., Sandison G. A., Farr J. B., and Edwards A. C., “Scattered neutron dose equivalent from an active scanning proton beam delivery system,” Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 30, 326–330 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

