Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain
- PMID: 24322588
- PMCID: PMC3947586
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000101
Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain
Abstract
In the last decade, preclinical investigations of electroacupuncture mechanisms on persistent tissue injury (inflammatory), nerve injury (neuropathic), cancer, and visceral pain have increased. These studies show that electroacupuncture activates the nervous system differently in health than in pain conditions, alleviates both sensory and affective inflammatory pain, and inhibits inflammatory and neuropathic pain more effectively at 2 to 10 Hz than at 100 Hz. Electroacupuncture blocks pain by activating a variety of bioactive chemicals through peripheral, spinal, and supraspinal mechanisms. These include opioids, which desensitize peripheral nociceptors and reduce proinflammatory cytokines peripherally and in the spinal cord, and serotonin and norepinephrine, which decrease spinal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit GluN1 phosphorylation. Additional studies suggest that electroacupuncture, when combined with low dosages of conventional analgesics, provides effective pain management which can forestall the side effects of often-debilitating pharmaceuticals.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
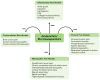
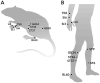
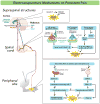
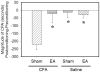


Comment in
-
About acupuncture and electroacupuncture.Anesthesiology. 2014 Sep;121(3):662. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000341. Anesthesiology. 2014. PMID: 25222677 No abstract available.
-
In reply.Anesthesiology. 2014 Sep;121(3):662-3. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000342. Anesthesiology. 2014. PMID: 25222678 No abstract available.
References
-
- Institute of medicine. (US) committee on advancing pain research, care, and education: Relieving pain in America: A blueprint for transforming prevention, care, education, and research. Washington DC: National Academies Press (US); 2011. - PubMed
-
- Berman BM, Lao L, Langenberg P, Wen Lin L, Gilpin AMK, Hochberg MC. Effectiveness of acupuncture as adjunctive therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee. Ann Intern Med. 2004;141:901–10. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PM, Barbara B, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults and children: United States, 2007. National Health Statistics Reports. 2008;12:1–24. - PubMed
-
- Taguchi R, Taguchi T, Kitakoji H. Involvement of peripheral opioid receptors in electroacupuncture analgesia for carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia. Brain Res. 2010;1355:97–103. - PubMed
-
- Sekido R, Ishimaru K, Sakita M. Differences of electroacupuncture-induced analgesic effect in normal and inflammatory conditions in rats. Am J Chin Med. 2003;31:955–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

