Genetically encoded fluorescent probe to visualize intracellular phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate localization and dynamics
- PMID: 24324172
- PMCID: PMC3876232
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1311864110
Genetically encoded fluorescent probe to visualize intracellular phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate localization and dynamics
Abstract
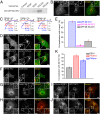
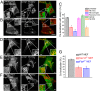
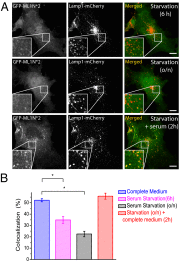
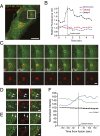
Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate [PI(3,5)P2] is a low-abundance phosphoinositide presumed to be localized to endosomes and lysosomes, where it recruits cytoplasmic peripheral proteins and regulates endolysosome-localized membrane channel activity. Cells lacking PI(3,5)P2 exhibit lysosomal trafficking defects, and human mutations in the PI(3,5)P2-metabolizing enzymes cause lysosome-related diseases. The spatial and temporal dynamics of PI(3,5)P2, however, remain unclear due to the lack of a reliable detection method. Of the seven known phosphoinositides, only PI(3,5)P2 binds, in the low nanomolar range, to a cytoplasmic phosphoinositide-interacting domain (ML1N) to activate late endosome and lysosome (LEL)-localized transient receptor potential Mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) channels. Here, we report the generation and characterization of a PI(3,5)P2-specific probe, generated by the fusion of fluorescence tags to the tandem repeats of ML1N. The probe was mainly localized to the membranes of Lamp1-positive compartments, and the localization pattern was dynamically altered by either mutations in the probe, or by genetically or pharmacologically manipulating the cellular levels of PI(3,5)P2. Through the use of time-lapse live-cell imaging, we found that the localization of the PI(3,5)P2 probe was regulated by serum withdrawal/addition, undergoing rapid changes immediately before membrane fusion of two LELs. Our development of a PI(3,5)P2-specific probe may facilitate studies of both intracellular signal transduction and membrane trafficking in the endosomes and lysosomes.
Keywords: PIKfyve; TRP channel; vesicle fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Visualization of Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-Bisphosphate Dynamics by a Tandem ML1N-Based Fluorescent Protein Probe in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Physiol. 2017 Jul 1;58(7):1185-1195. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcx011. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28158631 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila TRPML forms PI(3,5)P2-activated cation channels in both endolysosomes and plasma membrane.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 14;289(7):4262-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.506501. Epub 2013 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24375408 Free PMC article.
-
PI(3,5)P(2) controls membrane trafficking by direct activation of mucolipin Ca(2+) release channels in the endolysosome.Nat Commun. 2010 Jul 13;1(4):38. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1037. Nat Commun. 2010. PMID: 20802798 Free PMC article.
-
TRPML1: an ion channel in the lysosome.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:631-45. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_24. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756723 Review.
-
TRPML2 and mucolipin evolution.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:647-58. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_25. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756724 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid agonism: The PIP2 paradigm of ligand-gated ion channels.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1851(5):620-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25633344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Septins promote macropinosome maturation and traffic to the lysosome by facilitating membrane fusion.J Cell Biol. 2016 Aug 29;214(5):517-27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201603030. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27551056 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid composition of the cancer cell membrane.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2020 Oct;52(5):321-342. doi: 10.1007/s10863-020-09846-4. Epub 2020 Jul 26. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32715369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological targeting PIKfyve and tubulin as an effective treatment strategy for double-hit lymphoma.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Jan 28;8(1):39. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00833-9. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35091546 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring lipid-protein interactions in plant membranes.J Exp Bot. 2024 Sep 11;75(17):5251-5266. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae199. J Exp Bot. 2024. PMID: 38708855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Di Paolo G, De Camilli P. Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature. 2006;443(7112):651–657. - PubMed
-
- Lemmon MA. Membrane recognition by phospholipid-binding domains. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(2):99–111. - PubMed
-
- Stauffer TP, Ahn S, Meyer T. Receptor-induced transient reduction in plasma membrane PtdIns(4,5)P2 concentration monitored in living cells. Curr Biol. 1998;8(6):343–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

