Sorting of β1-adrenergic receptors is mediated by pathways that are either dependent on or independent of type I PDZ, protein kinase A (PKA), and SAP97
- PMID: 24324269
- PMCID: PMC3900972
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.513481
Sorting of β1-adrenergic receptors is mediated by pathways that are either dependent on or independent of type I PDZ, protein kinase A (PKA), and SAP97
Abstract
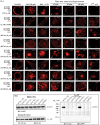
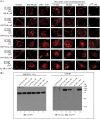
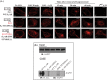
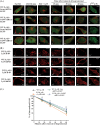
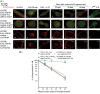
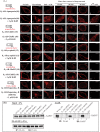
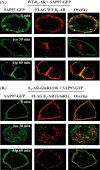
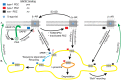
The β1-adrenergic receptor (β1-AR) is a target for treatment of major cardiovascular diseases, such as heart failure and hypertension. Recycling of agonist-internalized β1-AR is dependent on type I PSD-95/DLG/ZO1 (PDZ) in the C-tail of the β1-AR and on protein kinase A (PKA) activity (Gardner, L. A., Naren, A. P., and Bahouth, S. W. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 5085-5099). We explored the effects of point mutations in the PDZ and in the activity of PKA on recycling of the β1-AR and its binding to the PDZ-binding protein SAP97. These studies indicated that β1-AR recycling was inhibited by PKA inhibitors and by mutations in the PDZ that interfered with SAP97 binding. The trafficking effects of short sequences differing in PDZ and SAP97 binding were examined using chimeric mutant β1-AR. β1-AR chimera containing the type I PDZ of the β2-adrenergic receptor that does not bind to SAP97 failed to recycle except when serine 312 was mutated to aspartic acid. β1-AR chimera with type I PDZ sequences from the C-tails of aquaporin-2 or GluR1 recycled in a SAP97- and PKA-dependent manner. Non-PDZ β1-AR chimera derived from μ-opioid, dopamine 1, or GluR2 receptors promoted rapid recycling of chimeric β1-AR in a SAP97- and PKA-independent manner. Moreover, the nature of the residue at position -3 in the PDZ regulated whether the β1-AR was internalized alone or in complex with SAP97. These results indicate that divergent pathways were involved in trafficking the β1-AR and provide a roadmap for its trafficking via type I PDZs versus non-PDZs.
Keywords: Adrenergic Receptor; Confocal Microscopy; G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR); Protein Kinase A (PKA); Trafficking.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assembly of an SAP97-AKAP79-cAMP-dependent protein kinase scaffold at the type 1 PSD-95/DLG/ZO1 motif of the human beta(1)-adrenergic receptor generates a receptosome involved in receptor recycling and networking.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 16;282(7):5085-5099. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608871200. Epub 2006 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17170109
-
Identification of novel transplantable GPCR recycling motif for drug discovery.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;120:22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.09.011. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27645110 Free PMC article.
-
SAP97 controls the trafficking and resensitization of the beta-1-adrenergic receptor through its PDZ2 and I3 domains.PLoS One. 2013 May 16;8(5):e63379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063379. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23696820 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of SAP97 anchored multiprotein complexes in regulating cardiorenal signaling and trafficking networks.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Feb;208:115406. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115406. Epub 2022 Dec 31. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36596415 Review.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
Cited by
-
Updated Insight into the Physiological and Pathological Roles of the Retromer Complex.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 25;18(8):1601. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081601. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28757549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Paradigms Governing β1-Adrenergic Receptor Trafficking in Primary Adult Rat Cardiac Myocytes.Mol Pharmacol. 2018 Aug;94(2):862-875. doi: 10.1124/mol.118.112045. Epub 2018 May 30. Mol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29848777 Free PMC article.
-
A long lasting β1 adrenergic receptor stimulation of cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) signal in cardiac myocytes.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 23;289(21):14771-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.542589. Epub 2014 Apr 8. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24713698 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: Role of intracellular scaffolding proteins in the regulation of endocrine G protein-coupled receptor signaling.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Jun;29(6):814-30. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1091. Epub 2015 May 5. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25942107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PDZ Domain Protein SYNJ2BP Regulates GRK-Dependent Sst2A Phosphorylation and Downstream MAPK Signaling.Endocrinology. 2021 Feb 1;162(2):bqaa229. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa229. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 33313679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanyaloglu A. C., von Zastrow M. (2008) Regulation of GPCRs by endocytic membrane trafficking and its potential implications. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 48, 537–568 - PubMed
-
- Violin J. D., Ren X. R., Lefkowitz R. J. (2006) G-protein-coupled receptor kinase specificity for β-arrestin recruitment to the β2-adrenergic receptor revealed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 20577–20588 - PubMed
-
- Ferguson S. S., Downey W. E., 3rd, Colapietro A. M., Barak L. S., Ménard L., Caron M. G. (1996) Role of β-arrestin in mediating agonist-promoted G protein-coupled receptor internalization. Science 271, 363–366 - PubMed
-
- Cao T. T., Deacon H. W., Reczek D., Bretscher A., von Zastrow M. (1999) A kinase-regulated PDZ-domain interaction controls endocytic sorting of the β2-adrenergic receptor. Nature 401, 286–290 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

