Rheumatoid factors: clinical applications
- PMID: 24324289
- PMCID: PMC3845430
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/726598
Rheumatoid factors: clinical applications
Abstract
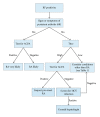
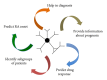
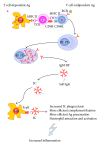
Rheumatoid factors are antibodies directed against the Fc region of immunoglobulin G. First detected in patients with rheumatoid arthritis 70 years ago, they can also be found in patients with other autoimmune and nonautoimmune conditions, as well as in healthy subjects. Rheumatoid factors form part of the workup for the differential diagnosis of arthropathies. In clinical practice, it is recommended to measure anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factors together because anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies alone are only moderately sensitive, and the combination of the two markers improves diagnostic accuracy, especially in the case of early rheumatoid arthritis. Furthermore, different rheumatoid factor isotypes alone or in combination can be helpful when managing rheumatoid arthritis patients, from the time of diagnosis until deciding on the choice of therapeutic strategy.
Figures
References
-
- Dörner T, Egerer K, Feist E, Burmester GR. Rheumatoid factor revisited. Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 2004;16(3):246–253. - PubMed
-
- Waaler E. On the occurrence of a factor in human serum activating the specific agglutination of sheep blood corpuscles. Acta Pathologica Microbiologica Scandinavica. 1940;17(2):172–188. - PubMed
-
- Rose HM, Ragan C, et al. Differential agglutination of normal and sensitized sheep erythrocytes by sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 1948;68(1):1–6. - PubMed
-
- Pike RM, Sulkin SE, Coggeshall HC. Serological reactions in rheumatoid arthritis; factors affecting the agglutination of sensitized sheep erythrocytes in rheumatid-arthritis serum. Journal of Immunology. 1949;63(4):441–446. - PubMed
-
- Ball J, Bloch KJ, Burch TA, Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS, Tsigalidou V. Comparative studies of serologic tests for rheumatoid disease. II. A comparison of the bentonite flocculation test and the sensitized sheep cell agglutination test. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 1962;5:61–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

