Potential Roles of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni in Abrogating Insulin Resistance and Diabetes: A Review
- PMID: 24324517
- PMCID: PMC3845826
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/718049
Potential Roles of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni in Abrogating Insulin Resistance and Diabetes: A Review
Abstract
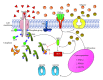
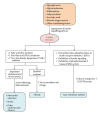
Insulin resistance is a key factor in metabolic disorders like hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia, which are promoted by obesity and may later lead to Type II diabetes mellitus. In recent years, researchers have identified links between insulin resistance and many noncommunicable illnesses other than diabetes. Hence, studying insulin resistance is of particular importance in unravelling the pathways employed by such diseases. In this review, mechanisms involving free fatty acids, adipocytokines such as TNF α and PPAR γ and serine kinases like JNK and IKK β , asserted to be responsible in the development of insulin resistance, will be discussed. Suggested mechanisms for actions in normal and disrupted states were also visualised in several manually constructed diagrams to capture an overall view of the insulin-signalling pathway and its related components. The underlying constituents of medicinal significance found in the Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni plant (among other plants that potentiate antihyperglycemic activities) were explored in further depth. Understanding these factors and their mechanisms may be essential for comprehending the progression of insulin resistance towards the development of diabetes mellitus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stevia rebaudiana extract attenuate metabolic disorders in diabetic rats via modulation of glucose transport and antioxidant signaling pathways and aquaporin-2 expression in two extrahepatic tissues.J Food Biochem. 2020 Aug;44(8):e13252. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13252. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Food Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32515037
-
Toxicological evaluation of ethanolic extract from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves: Genotoxicity and subchronic oral toxicity.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017 Jun;86:253-259. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.03.021. Epub 2017 Mar 25. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28351677
-
smRNAome profiling to identify conserved and novel microRNAs in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Nov 1;12:197. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-197. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 23116282 Free PMC article.
-
Maladaptive immune and inflammatory pathways lead to cardiovascular insulin resistance.Metabolism. 2013 Nov;62(11):1543-52. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23932846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological activity of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni and their relationship to health.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Aug 13;57(12):2680-2690. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2015.1072083. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017. PMID: 26479769 Review.
Cited by
-
Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni: A Natural Alternative for Treating Diseases Associated with Metabolic Syndrome.J Med Food. 2017 Oct;20(10):933-943. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2016.0171. Epub 2017 Aug 9. J Med Food. 2017. PMID: 28792778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steviol glycosides as an alternative osmotic agent for peritoneal dialysis fluid.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 16;13:868374. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.868374. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36052133 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Stevia Consumption on Gut Bacteria: Friend or Foe?Microorganisms. 2022 Mar 30;10(4):744. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10040744. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35456796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of stevia on synaptic plasticity and NADPH oxidase level of CNS in conditions of metabolic disorders caused by fructose.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Dec 19;17(1):540. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-2049-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 29258552 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni Possess Insulin-Mimetic and Antioxidant Activities in Rat Cardiac Fibroblasts.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:3724545. doi: 10.1155/2017/3724545. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28947927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leney SE, Tavaré JM. The molecular basis of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake: signalling, trafficking and potential drug targets. Journal of Endocrinology. 2009;203(1):1–18. - PubMed
-
- Goodrich KM, Crowley SK, Lee D-C, Sui XS, Hooker SP, Blair SN. Associations of cardiorespiratory fitness and parental history of diabetes with risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2012;95(3):425–431. - PubMed
-
- Hamman RF. Genetic and environmental determinants of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) Diabetes/Metabolism Reviews. 1992;8(4):287–338. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

