Human endogenous retrovirus protein activates innate immunity and promotes experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in mice
- PMID: 24324591
- PMCID: PMC3855614
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080128
Human endogenous retrovirus protein activates innate immunity and promotes experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in mice
Abstract
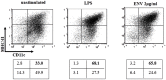
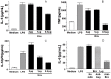
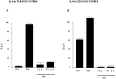
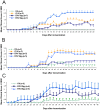
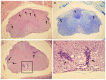
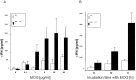
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a complex multifactorial disease of the central nervous system (CNS) for which animal models have mainly addressed downstream immunopathology but not potential inducers of autoimmunity. In the absence of a pathogen known to cause neuroinflammation in MS, Mycobacterial lysate is commonly used in the form of complete Freund's adjuvant to induce autoimmunity to myelin proteins in Experimental Allergic Encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model for MS. The present study demonstrates that a protein from the human endogenous retrovirus HERV-W family (MSRV-Env) can be used instead of mycobacterial lysate to induce autoimmunity and EAE in mice injected with MOG, with typical anti-myelin response and CNS lesions normally seen in this model. MSRV-Env was shown to induce proinflammatory response in human macrophage cells through TLR4 activation pathway. The present results demonstrate a similar activation of murine dendritic cells and show the ability of MSRV-Env to trigger EAE in mice. In previous studies, MSRV-Env protein was reproducibly detected in MS brain lesions within microglia and perivascular macrophages. The present results are therefore likely to provide a model for MS, in which the upstream adjuvant triggering neuroinflammation is the one detected in MS active lesions. This model now allows pre-clinical studies with therapeutic agents targeting this endogenous retroviral protein in MS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Costenbader KH, Gay S, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Iaccarino L, Doria A (2012) Genes, epigenetic regulation and environmental factors: which is the most relevant in developing autoimmune diseases? Autoimmun Rev 11: 604–609. - PubMed
-
- Kuhlmann T, Miron V, Cui Q, Wegner C, Antel J, et al. (2008) Differentiation block of oligodendroglial progenitor cells as a cause for remyelination failure in chronic multiple sclerosis. Brain 131: 1749–1758. - PubMed
-
- Romme Christensen J, Bornsen L, Khademi M, Olsson T, Jensen PE, et al. (2012) CSF inflammation and axonal damage are increased and correlate in progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler - PubMed
-
- Elong Ngono A, Pettre S, Salou M, Bahbouhi B, Soulillou JP, et al. (2012) Frequency of circulating autoreactive T cells committed to myelin determinants in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients. Clin Immunol 144: 117–126. - PubMed
-
- Baker D, Gerritsen W, Rundle J, Amor S (2011) Critical appraisal of animal models of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 17: 647–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

