Tyrosine phosphorylation modulates the vascular responses of mesenteric arteries from human colorectal tumors
- PMID: 24324963
- PMCID: PMC3842070
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/545983
Tyrosine phosphorylation modulates the vascular responses of mesenteric arteries from human colorectal tumors
Abstract
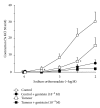
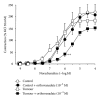
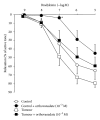
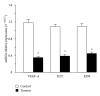
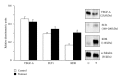
The aim of this study was to analyze whether tyrosine phosphorylation in tumoral arteries may modulate their vascular response. To do this, mesenteric arteries supplying blood flow to colorectal tumors or to normal intestine were obtained during surgery and prepared for isometric tension recording in an organ bath. Increasing tyrosine phosphorylation with the phosphatase inhibitor, sodium orthovanadate produced arterial contraction which was lower in tumoral than in control arteries, whereas it reduced the contraction to noradrenaline in tumoral but not in control arteries and reduced the relaxation to bradykinin in control but not in tumoral arteries. Protein expression of VEGF-A and of the VEGF receptor FLT1 was similar in control and tumoral arteries, but expression of the VEGF receptor KDR was increased in tumoral compared with control arteries. This suggests that tyrosine phosphorylation may produce inhibition of the contraction in tumoral mesenteric arteries, which may increase blood flow to the tumor when tyrosine phosphorylation is increased by stimulation of VEGF receptors.
Figures
References
-
- Choura M, Rebaï A. Receptor tyrosine kinases: from biology to pathology. Journal of Receptors and Signal Transduction. 2011;31(6):387–394. - PubMed
-
- Madhusudan S, Ganesan TS. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Clinical Biochemistry. 2004;37(7):618–635. - PubMed
-
- Elberg G, Li J, Leibovitch A, Shechter Y. Non-receptor cytosolic protein tyrosine kinases from various rat tissues. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1995;1269(3):299–306. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Mizumoto K, Kakutani T, Hasegawa A, Ogawa K, Hatano Y. Comparison of the effects of isoflurane and sevoflurane on protein tyrosine phosphorylation-mediated vascular contraction. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 2005;49(6):852–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

