Validity of 2D lateral cephalometry in orthodontics: a systematic review
- PMID: 24325757
- PMCID: PMC3882109
- DOI: 10.1186/2196-1042-14-31
Validity of 2D lateral cephalometry in orthodontics: a systematic review
Abstract
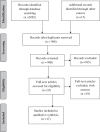
Lateral cephalometric radiography is commonly used as a standard tool in orthodontic assessment and treatment planning. The aim of this study was to evaluate the available scientific literature and existing evidence for the validation of using lateral cephalometric imaging for orthodontic treatment planning. The secondary objective was to determine the accuracy and reliability of this technique. We did not attempt to evaluate the value of this radiographic technique for other purposes. A literature search was performed using specific keywords on electronic databases: Ovid MEDLINE, Scopus and Web of Science. Two reviewers selected relevant articles, corresponding to predetermined inclusion criteria. The electronic search was followed by a hand search of the reference lists of relevant papers. Two reviewers assessed the level of evidence of relevant publications as high, moderate or low. Based on this, the evidence grade for diagnostic efficacy was rated as strong, moderately strong, limited or insufficient. The initial search revealed 784 articles listed in MEDLINE (Ovid), 1,034 in Scopus and 264 articles in the Web of Science. Only 17 articles met the inclusion criteria and were selected for qualitative synthesis. Results showed seven studies on the role of cephalometry in orthodontic treatment planning, eight concerning cephalometric measurements and landmark identification and two on cephalometric analysis. It is surprising that, notwithstanding the 968 articles published in peer-reviewed journals, scientific evidence on the usefulness of this radiographic technique in orthodontics is still lacking, with contradictory results. More rigorous research on a larger study population should be performed to achieve full evidence on this topic.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous