Population prevalence and control of cardiovascular risk factors: what electronic medical records tell us
- PMID: 24325864
- PMCID: PMC6983525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aprim.2013.06.004
Population prevalence and control of cardiovascular risk factors: what electronic medical records tell us
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the prevalence, control, and management of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2).
Design: Cross-sectional analysis of all individuals attended in the Catalan primary care centers between 2006 and 2009.
Location: History of cardiovascular diseases, diagnosis and treatment of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, DM2, lipid profile, glycemia and blood pressure data were extracted from electronic medical records. Age-standardized prevalence and levels of management and control were estimated.
Participants: Individuals aged 35-74 years using primary care databases.
Main measures: A total of 2,174,515 individuals were included (mean age 52 years [SD 11], 47% men).
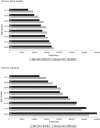
Results: Hypertension was the most prevalent cardiovascular risk factor (39% in women, 41% in men) followed by hypercholesterolemia (38% and 40%) and DM2 (12% and 16%), respectively. Diuretics and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors were most often prescribed for hypertension control (<140/90mmHg, achieved in 68% of men and 60% of women treated). Hypercholesterolemia was controlled (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol <130mg/dl) in just 31% of men and 26% of women with no history of cardiovascular disease, despite lipid-lowering treatment, primarily (90%) with statins. The percentage of women and men with DM2 and with glycated hemoglobin <7% was 64.7% and 59.2%, respectively; treatment was predominantly with oral hypoglycemic agents alone (70%), or combined with insulin (15%).
Conclusions: Hypertension was the most prevalent cardiovascular risk factor in the Catalan population attended at primary care centers. About two thirds of individuals with hypertension or DM2 were adequately controlled; hypercholesterolemia control was particularly low.
Objetivos: Analizar la prevalencia, control y manejo de la hipertensión arterial, hipercolesterolemia y diabetes mellitus tipo 2.
Diseño: Análisis transversal de todos los individuos atendidos en centros de atención primaria entre 2006 y 2009.
Emplazamiento: Se extrajo de la historia clínica electrónica los antecedentes de enfermedad cardiovascular, el diagnóstico y tratamiento de la hipertensión arterial, hipercolesterolemia, diabetes mellitus tipo 2, el perfil lipídico, la glicemia y la presión arterial. Las prevalencias y las variables de manejo y control se estandarizaron por edad.
Participantes: Individuos de 35 a 74 años registrados en las bases de datos de atención primaria.
Mediciones principales: Se analizaron registros de 2.174.515 de individuos (47% hombres, edad media 52 años (DE 11)).
Resultados: La hipertensión arterial fue el factor de riesgo más prevalente (39% en mujeres y 41% en hombres), seguido de la hipercolesterolemia (38% y 40%) y la diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (12% y 16%), respectivamente. Los diuréticos y los inhibidores de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina fueron los fármacos más frecuentemente recetados para el control de la presión arterial (68% de hombres y 60% de mujeres presentaron valores <140/90 mmHg). Sólo el 31% de los hombres y el 26% de las mujeres sin antecedentes de enfermedad cardiovascular presentaron hipercolesterolemia controlada (colesterol de las lipoproteínas de baja densidad <130 mg/dl), a pesar del porcentaje de tratamiento con estatinas (90%). EL porcentaje de mujeres y hombres con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 y hemoglobina glicada <7% era de 64.7% y 59.2%, respectivamente; el tratamiento se realizó predominantemente con antidiabéticos orales únicamente (70%) o asociados con insulina (15%).
Conclusiones: La hipertensión arterial fue el factor de riesgo cardiovascular más prevalente en población catalana atendida en centros de atención primaria. Alrededor de dos tercios de los individuos con hipertensión arterial o diabetes mellitus tipo 2 estaban adecuadamente controlados; mientras que el control de la hipercolesterolemia fue especialmente bajo.
Keywords: Atención Primaria; Diabetes Mellitus tipo 2; Diabetes mellitus type 2; Electronic Health Records; Hipercolesterolemia; Hipertensión; Historia clínica electrónica; Hypercholesterolemia; Hypertension; Prevalence; Prevalencia; Primary health care.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier España, S.L. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization; Geneva: 2000. World Health Statistics. Monograph on the Internet. Available from: http://www.who.int/ncd_surveillance/infobase/web/InfoBaseCommon/ [cited 01.08.06]
-
- INEbase Instituto Nacional de Estadística (INE). Available from: http://www.ine.es/inebmenu/indice.htm [cited 17 Ago 2012].
-
- Dégano I.R., Elosua R., Marrugat J. Epidemiology of acute coronary syndrome in Spain: estimation of the number of cases and trends from 2005 to 2049. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2013;66:472–481. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S., Hawken S., Ounpuu S., Dans T., Avezum A., Lanas F. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case–control study. Lancet. 2004;364:937–952. - PubMed
-
- Goff D.C, Jr., Brass L., Braun L.T., Croft J.B., Flesch J.D., Fowkes F.G. Essential features of a surveillance system to the support the prevention and management of heart disease and stroke: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Epidemiology and Prevention, Stroke and Cardiovascular Nursing and the Interdisciplinary Working Groups on Quality of care and Outcomes Research and Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease. Circulation. 2007;115:127–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

