Empyema necessitans: very late complication of pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 24326441
- PMCID: PMC3863066
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-202072
Empyema necessitans: very late complication of pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
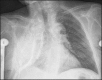
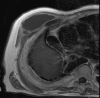
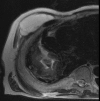
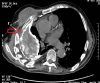
Empyema necessitans is a rare clinical finding nowadays. We report the case of a patient admitted in our ward for investigation of an unknown onset anterior chest wall mass, with no accompanying signs or symptoms. It is noteworthy that the patient had had pulmonary tuberculosis submitted to thoracoplasty more than 60 years before. Thoracic MRI showed a large heterogeneous mass, with a thick wall and internal septations located at the right anterior chest wall, as well as a heterogeneous content inside the right pleural cavity, with direct communication between both. An aspirative puncture of both masses was performed, with positive cultures for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, thus leading to the diagnosis of pleural tuberculosis with anterior chest wall empyema necessitans. A drain was inserted and antibiotics started. This case draws our attention to a very rare complication of pulmonary tuberculosis and its surgical treatment, though it aroused many decades after primary infection.
Figures

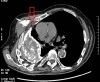
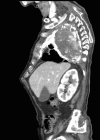
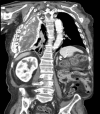
References
-
- Sahn SA, Iseman MD. Tuberculous empyema. Semin Respir Infect 1999;14:82–7 - PubMed
-
- Scott A, Kono DO, Trenton D, et al. Contemporary empyema necessitatis. Am J Med 2007;120:303–5 - PubMed
-
- Tezel C, Kiral H, Tezel Y, et al. Case review of an old disease: empyema necessitates. Emerg Med J 2008;25:114. - PubMed
-
- Reyes CV. Cutaneous tumefaction in empyema necessitatis. Int J Dermatol 2007;46:1294–7 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
