Heart beats in the cloud: distributed analysis of electrophysiological 'Big Data' using cloud computing for epilepsy clinical research
- PMID: 24326538
- PMCID: PMC3932471
- DOI: 10.1136/amiajnl-2013-002156
Heart beats in the cloud: distributed analysis of electrophysiological 'Big Data' using cloud computing for epilepsy clinical research
Abstract
Objective: The rapidly growing volume of multimodal electrophysiological signal data is playing a critical role in patient care and clinical research across multiple disease domains, such as epilepsy and sleep medicine. To facilitate secondary use of these data, there is an urgent need to develop novel algorithms and informatics approaches using new cloud computing technologies as well as ontologies for collaborative multicenter studies.
Materials and methods: We present the Cloudwave platform, which (a) defines parallelized algorithms for computing cardiac measures using the MapReduce parallel programming framework, (b) supports real-time interaction with large volumes of electrophysiological signals, and (c) features signal visualization and querying functionalities using an ontology-driven web-based interface. Cloudwave is currently used in the multicenter National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke (NINDS)-funded Prevention and Risk Identification of SUDEP (sudden unexplained death in epilepsy) Mortality (PRISM) project to identify risk factors for sudden death in epilepsy.
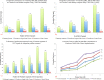
Results: Comparative evaluations of Cloudwave with traditional desktop approaches to compute cardiac measures (eg, QRS complexes, RR intervals, and instantaneous heart rate) on epilepsy patient data show one order of magnitude improvement for single-channel ECG data and 20 times improvement for four-channel ECG data. This enables Cloudwave to support real-time user interaction with signal data, which is semantically annotated with a novel epilepsy and seizure ontology.
Discussion: Data privacy is a critical issue in using cloud infrastructure, and cloud platforms, such as Amazon Web Services, offer features to support Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act standards.
Conclusion: The Cloudwave platform is a new approach to leverage of large-scale electrophysiological data for advancing multicenter clinical research.
Keywords: Cloudwave; Electrophsyiological Big Data; Epilepsy and Seizure; MapReduce; Ontology; SUDEP.
Figures





References
-
- Nature Editorial Community cleverness required. Nature 2008;455:1. - PubMed
-
- Madden S. From databases to Big Data. IEEE Internet Comput 2012;16:4–6
-
- Agrawal D, Bernstein P, Bertino E, et al. Challenges and Opportunities with Big Data. CRA white paper 2012
-
- Ferrucci D, Brown E, Chu-Carroll J, et al. Building Watson: an overview of the DeepQA project. AI Mag 2010;31:59–79
-
- Cohen J, Dolan B, Dunlap M, et al. MAD skills: new analysis practices for Big Data. Proc VLDB Endowment 2009;2:1481–92
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

