Janus kinases: an ideal target for the treatment of autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 24326567
- PMCID: PMC4181323
- DOI: 10.1038/jidsymp.2013.29
Janus kinases: an ideal target for the treatment of autoimmune diseases
Abstract
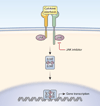
Cytokines have pivotal roles in the maintenance of an appropriate immune response. Targeting cytokine receptors has been an effective means of treating immune-related disorders. In the past few years, research efforts have been directed toward cytokines' intracellular signaling pathways and, in particular, the JAK-STAT (Janus kinase-signal transducers and activation of transcription) signaling cascade. Recently, spearheaded by the development of effective drugs in cancer treatment, it has become clear that the targeting of intracellular protein kinases is a very attractive and feasible possibility for the treatment of autoimmune disorders. The targeting of the Janus kinases (JAKs) has been quite successful and two JAK inhibitors are now approved to be used in humans. Interestingly, although some of the inhibitors developed and tested to date have been shown to target more than one kinase, this promiscuity does not appear to be problematic. Novel second-generation, more specific inhibitors are under development, and in the next few years, we expect this class of drugs to become a powerful tool in the hands of clinician treating autoimmune diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Fleischmann R, Kremer J, Cush J, Schulze-Koops H, Connell CA, Bradley JD, et al. Placebo-controlled trial of tofacitinib monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. The New England journal of medicine. 2012;367:495–507. - PubMed
-
- Harrison C, Kiladjian JJ, Al-Ali HK, Gisslinger H, Waltzman R, Stalbovskaya V, et al. JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. The New England journal of medicine. 2012;366:787–798. - PubMed
-
- Karaman MW, Herrgard S, Treiber DK, Gallant P, Atteridge CE, Campbell BT, et al. A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nature biotechnology. 2008;26:127–132. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;352:1779–1790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

