Safety and pharmacokinetics of escalating doses of human recombinant nerve growth factor eye drops in a double-masked, randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 24327173
- PMCID: PMC4030100
- DOI: 10.1007/s40259-013-0079-5
Safety and pharmacokinetics of escalating doses of human recombinant nerve growth factor eye drops in a double-masked, randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background and objectives: Nerve growth factor (NGF) is a neurotrophin with therapeutic possibilities that extend from the nervous system to the eye. We tested the safety, maximal tolerated dose, pharmacokinetics, and antigenicity of a novel human recombinant NGF (rhNGF) eye-drop formulation in a phase I study.
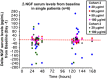
Methods: This prospective, randomized, double-masked, vehicle-controlled trial, sponsored by Dompé SpA (registered as NCT01744704 at ClinicalTrials.gov), enrolled 74 healthy volunteers (24 females, 50 males, age 40.2 ± 11.8 years). Subjects were randomized in three cohorts to receive (1) a single eye-drop containing 0.0175, 0.175, or 0.7 μg rhNGF; (2) a single ascending dose of rhNGF eye drops three times a day for 1 day (total daily dose 2.1, 6.3, or 18.9 μg), or vehicle; or (3) a multiple ascending dose of rhNGF eye drops three times a day for 5 days (total dose 10.5, 31.5, or 94.5 μg), or vehicle. Outcome measures included blood chemistry, urinalyses, vital signs, electrocardiograms (ECGs), serum NGF antibodies, ocular and systemic adverse events (AEs), visual acuity, tear function, intraocular pressure, fundus oculi, and ocular symptoms.
Results: Administration of rhNGF eye drops did not result in a significant increase of circulating NGF levels and no antidrug antibodies were detected in serum. No serious AEs were recorded, and a few mild, transient ocular AEs related to rhNGF administration were reported only at the highest concentration.
Conclusions: rhNGF eye drops were well tolerated, with no detectable clinical evidence of systemic AEs. These results pave the way for the development of clinical trials on rhNGF in ophthalmology.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical