Seven transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor repertoire of gastric ghrelin cells
- PMID: 24327954
- PMCID: PMC3854997
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2013.08.006
Seven transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor repertoire of gastric ghrelin cells
Abstract
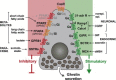
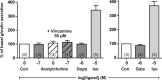
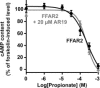
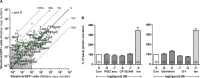
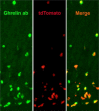
The molecular mechanisms regulating secretion of the orexigenic-glucoregulatory hormone ghrelin remain unclear. Based on qPCR analysis of FACS-purified gastric ghrelin cells, highly expressed and enriched 7TM receptors were comprehensively identified and functionally characterized using in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo methods. Five Gαs-coupled receptors efficiently stimulated ghrelin secretion: as expected the β1-adrenergic, the GIP and the secretin receptors but surprisingly also the composite receptor for the sensory neuropeptide CGRP and the melanocortin 4 receptor. A number of Gαi/o-coupled receptors inhibited ghrelin secretion including somatostatin receptors SSTR1, SSTR2 and SSTR3 and unexpectedly the highly enriched lactate receptor, GPR81. Three other metabolite receptors known to be both Gαi/o- and Gαq/11-coupled all inhibited ghrelin secretion through a pertussis toxin-sensitive Gαi/o pathway: FFAR2 (short chain fatty acid receptor; GPR43), FFAR4 (long chain fatty acid receptor; GPR120) and CasR (calcium sensing receptor). In addition to the common Gα subunits three non-common Gαi/o subunits were highly enriched in ghrelin cells: GαoA, GαoB and Gαz. Inhibition of Gαi/o signaling via ghrelin cell-selective pertussis toxin expression markedly enhanced circulating ghrelin. These 7TM receptors and associated Gα subunits constitute a major part of the molecular machinery directly mediating neuronal and endocrine stimulation versus metabolite and somatostatin inhibition of ghrelin secretion including a series of novel receptor targets not previously identified on the ghrelin cell.
Keywords: 7TM, seven transmembrane segment; BAC, bacterial artificial chromosome; CCK, cholecystokinin; CFMB, (S)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3,3-dimethyl-N-(5-phenylthiazol-2-yl)butamide; CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide; CHBA, 3-chloro-5-hydroxybenzoic acid; Enteroendocrine; G protein signaling; GIP, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; GPCR; Ghrelin; Metabolites; PTx, Bordetella pertussis toxin; PYY, peptide YY; Secretion; hrGFP, humanized Renilla reniformis green fluorescent protein.
Figures






References
-
- Kojima M., Hosoda H., Date Y., Nakazato M., Matsuo H., Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402(6762):656–660. - PubMed
-
- Kirchner H., Heppner K.M., Tschop M.H. The role of ghrelin in the control of energy balance. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 2012;209:161–184. - PubMed
-
- Tschop M., Smiley D.L., Heiman M.L. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature. 2000;407(6806):908–913. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

