The thioredoxin system in neonatal lung disease
- PMID: 24328910
- PMCID: PMC4202924
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2013.5782
The thioredoxin system in neonatal lung disease
Abstract
Significance: Fetal lung development takes place in hypoxia meaning that premature birth is hyperoxia for the prematurely born infant. The most common respiratory morbidity afflicting premature infants is bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). Pathophysiologically, BPD represents the impact of injury, including O2 toxicity, to the immature developing lung that causes arrested lung development.
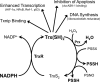
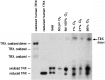
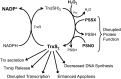
Recent advances: The thioredoxin (Trx) system, which is predominantly expressed in pulmonary epithelia in the newborn lung, acts as an antioxidant system; however, it is increasingly recognized as a key redox regulator of signal transduction and gene expression via thiol-disulfide exchange reactions.
Critical issues: This review focuses on the contribution of Trx family proteins toward normal and aberrant lung development, in particular, the roles of the Trx system in hyperoxic responses of alveolar epithelial cells, aberrant lung development in animal models of BPD, O2-dependent signaling processes, and possible therapeutic efficacy in preventing O2-mediated lung injury.
Future directions: The significant contribution of the Trx system toward redox regulation of key developmental pathways necessary for proper lung development suggests that therapeutic strategies focused on preserving pulmonary Trx function could significantly improve the outcomes of prematurely born human infants.
Figures
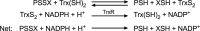


References
-
- Arner ES. Focus on mammalian thioredoxin reductases—important selenoproteins with versatile functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790: 495–526, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Arner ES. and Holmgren A. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem 267: 6102–6109, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Asikainen TM, Chang LY, Coalson JJ, Schneider BK, Waleh NS, Ikegami M, Shannon JM, Winter VT, Grubb P, Clyman RI, Yoder BA, Crapo JD, and White CW. Improved lung growth and function through hypoxia-inducible factor in primate chronic lung disease of prematurity. FASEB J 20: 1698–1700, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Asikainen TM. and White CW. Pulmonary antioxidant defenses in the preterm newborn with respiratory distress and bronchopulmonary dysplasia in evolution: implications for antioxidant therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal 6: 155–167, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Asikainen TM. and White CW. Antioxidant defenses in the preterm lung: role for hypoxia-inducible factors in BPD? Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203: 177–188, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

