Post-operative acute kidney injury and five-year risk of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke among elective cardiac surgical patients: a cohort study
- PMID: 24330762
- PMCID: PMC4057271
- DOI: 10.1186/cc13158
Post-operative acute kidney injury and five-year risk of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke among elective cardiac surgical patients: a cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: The prognostic impact of acute kidney injury (AKI) on long-term clinical outcomes remains controversial. We examined the five-year risk of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke after elective cardiac surgery complicated by AKI.
Methods: We conducted a cohort study among adult elective cardiac surgical patients without severe chronic kidney disease and/or previous heart or renal transplant surgery using data from population-based registries. AKI was defined by the Acute Kidney Injury Network (AKIN) criteria as a 50% increase in serum creatinine from baseline level, acute creatinine rise of ≥26.5 μmol/L (0.3 mg/dL) within 48 hours, and/or initiation of renal replacement therapy within five days after surgery. We followed patients from the fifth post-operative day until myocardial infarction, stroke or death within five years. Five-year risk was computed by the cumulative incidence method and compared with hazards ratios (HR) from a Cox proportional hazards regression model adjusting for propensity score.
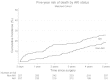
Results: A total of 287 (27.9%) of 1,030 patients developed AKI. Five-year risk of death was 26.5% (95% CI: 21.2 to 32.0) among patients with AKI and 12.1% (95% CI: 10.0 to 14.7) among patients without AKI. The corresponding adjusted HR of death was 1.6 (95% CI: 1.1 to 2.2). Five-year risk of myocardial infarction was 5.0% (95% CI: 2.9 to 8.1) among patients with AKI and 3.3% (95% CI: 2.1 to 4.8) among patients without AKI. Five-year risk of stroke was 5.0% (95% CI: 2.8 to 7.9) among patients with AKI and 4.2% (95% CI: 2.9 to 5.8) among patients without AKI. Adjusted HRs were 1.5 (95% CI: 0.7 to 3.2) of myocardial infarction and 0.9 (95% CI: 0.5 to 1.8) of stroke.
Conclusions: AKI, within five days after elective cardiac surgery, was associated with increased five-year mortality and a statistically insignificant increased risk of myocardial infarction. No association was seen with the risk of stroke.
Figures
Comment in
-
Renal function after elective total hip replacement.Acta Orthop. 2016 Jun;87(3):235-8. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2016.1155130. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Acta Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26937782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wijeysundera DN, Rao V, Beattie WS, Ivanov J, Karkouti K. Evaluating surrogate measures of renal dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2003;17:1265–1273. - PubMed
-
- Gallagher S, Jones DA, Lovell MJ, Hassan S, Wragg A, Kapur A, Uppal R, Yaqoob MM. The impact of acute kidney injury on midterm outcomes after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a matched propensity score analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013. [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical