Genistein decreases the breast cancer stem-like cell population through Hedgehog pathway
- PMID: 24331293
- PMCID: PMC4054948
- DOI: 10.1186/scrt357
Genistein decreases the breast cancer stem-like cell population through Hedgehog pathway
Abstract
Introduction: The existence of breast cancer stem-like cells (BCSCs) has profound implications for cancer prevention. Genistein, a predominant isoflavone found in soy products, has multiple robust anti-tumor effects in various cancers, especially in the breast and prostate cancer. In this study, we aimed to evaluate genistein inhibition of BCSCs and its potential mechanism by culturing MCF-7 breast cancer cells and implanting these cells into nude mice.
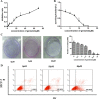
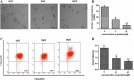
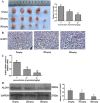
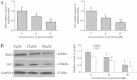
Methods: Cell counting, colony formation and cell apoptosis analysis were used to evaluate the effect of genistein on breast cancer cells’ growth, proliferation and apoptosis. We then used mammosphere formation assay and CD44CD24 staining to evaluate the effect of genistein on BCSCs in vitro. A nude mice xenograft model was employed to determine whether genistein could target BCSCs in vivo, as assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and immunohistochemical staining. The potential mechanism was investigated utilizing real-time PCR, western blotting analysis and immunohistochemical staining.
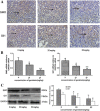
Results: Genistein inhibited the MCF-7 breast cancer cells’ growth and proliferation and promoted apoptosis. Both in vitro and in vivo genistein decreased breast cancer stem cells, and inhibited breast cancer stem-like cells through down-regulation of the Hedgehog-Gli1 Signaling Pathway.
Conclusions: We demonstrated for the first time that genistein inhibits BCSCs by down-regulating Hedgehog-Gli1 signaling pathway. These findings provide support and rationale for investigating the clinical application of genistein in treating breast cancer, and specifically by targeting breast cancer stem cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genistein inhibits the stemness properties of prostate cancer cells through targeting Hedgehog-Gli1 pathway.Cancer Lett. 2012 Oct 1;323(1):48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.03.037. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Cancer Lett. 2012. PMID: 22484470
-
Physalin A, 13,14-Seco-16, 24-Cyclo-Steroid, Inhibits Stemness of Breast Cancer Cells by Regulation of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway and Yes-Associated Protein 1 (YAP1).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 13;22(16):8718. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168718. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445421 Free PMC article.
-
Salinomycin exerts anticancer effects on human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cancer stem cells via modulation of Hedgehog signaling.Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Feb 25;228:100-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Chem Biol Interact. 2015. PMID: 25499043
-
Mechanisms of action of the soy isoflavone genistein: emerging role for its effects via transforming growth factor beta signaling pathways.Am J Clin Nutr. 1998 Dec;68(6 Suppl):1418S-1425S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/68.6.1418S. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998. PMID: 9848510 Review.
-
Genistein inhibits human prostate cancer cell detachment, invasion, and metastasis.Am J Clin Nutr. 2014 Jul;100 Suppl 1(1):431S-6S. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.113.071290. Epub 2014 May 28. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24871471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential of Phytochemicals in Oral Cancer Prevention and Therapy: A Review of the Evidence.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 6;10(8):1150. doi: 10.3390/biom10081150. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32781654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction Effects between Organochlorine Pesticides and Isoflavones In Vitro and In Vivo.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:6861702. doi: 10.1155/2016/6861702. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27597971 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic evaluation of phytochemicals in breast cancer remedy: current understanding and future perspectives.RSC Adv. 2018 Aug 22;8(52):29714-29744. doi: 10.1039/c8ra04879g. eCollection 2018 Aug 20. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35547279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The "Yin and Yang" of Natural Compounds in Anticancer Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Sep 21;10(10):346. doi: 10.3390/cancers10100346. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30248941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting cancer stem cells with dietary phytochemical - Repositioned drug combinations.Cancer Lett. 2018 Oct 1;433:53-64. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.06.034. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 29960048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lampe JW, Nishino Y, Ray RM, Wu C, Li W, Lin MG, Gao DL, Hu YW, Shannon J, Stalsberg H, Porter PL, Frankenfeld CL, Wahala K, Thomas DB. Plasma isoflavones and fibrocystic breast conditions and breast cancer among women in Shanghai, China. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;4:2579–2586. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0368. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim J. Protective effects of Asian dietary items on cancers – soy and ginseng. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2008;4:543–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

