The interleukin-1 family: back to the future
- PMID: 24332029
- PMCID: PMC3933951
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.010
The interleukin-1 family: back to the future
Abstract
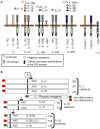
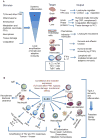
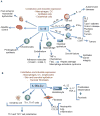
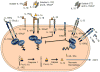
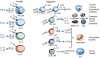
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a central mediator of innate immunity and inflammation. The IL-1 family includes seven ligands with agonist activity (IL-1α and IL-1β, IL-18, IL-33, IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ), three receptor antagonists (IL-1Ra, IL-36Ra, IL-38), and an anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-37). Members of the IL-1 Receptor (IL-1R) family include six receptor chains forming four signaling receptor complexes, two decoy receptors (IL-1R2, IL-18BP), and two negative regulators (TIR8 or SIGIRR, IL-1RAcPb). A tight regulation via receptor antagonists, decoy receptors, and signaling inhibitors ensures a balance between amplification of innate immunity and uncontrolled inflammation. All cells of the innate immune system express and/or are affected by IL-1 family members. Moreover, IL-1 family members play a key role in the differentiation and function of polarized innate and adaptive lymphoid cells. Here we will review the key properties of IL-1 family members, with emphasis on pathways of negative regulation and orchestration of innate and adaptive immunity.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Napolitani G, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F. Interleukins 1beta and 6 but not transforming growth factor-beta are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing human T helper cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:942–949. - PubMed
-
- Alves-Filho JC, Sonego F, Souto FO, Freitas A, Verri WA, Jr, Auxiliadora-Martins M, Basile-Filho A, McKenzie AN, Xu D, Cunha FQ, Liew FY. Interleukin-33 attenuates sepsis by enhancing neutrophil influx to the site of infection. Nat Med. 2010;16:708–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

