Plasma microparticle tissue factor activity in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies with and without clinical complications
- PMID: 24332063
- PMCID: PMC3925147
- DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2013.11.027
Plasma microparticle tissue factor activity in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies with and without clinical complications
Abstract
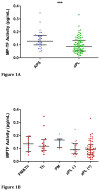
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is defined by the association of autoantibodies to certain phospholipid-binding proteins with arterial or venous thrombosis ('AT' or 'VT', respectively), and/or pregnancy-related morbidity (PM). Antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLA) promote activation of several cell types including monocytes, resulting in procoagulant tissue factor (TF) expression that may contribute to the vascular complications. Since TF synthesis by monocytes is frequently accompanied by release of TF-bearing microparticles, we hypothesized that plasma microparticle TF activity (MP-TF) may be elevated in APS patients and contribute to thrombosis and/or PM. Platelet-poor plasma specimens were obtained from 30 patients with definite APS and 72 patients with asymptomatic aPLA from the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Collaborative Registry (APSCORE). MP-TF was measured by an in-house factor Xa generation assay. The two groups were well matched for gender, age, ethnicity, proportions with underlying SLE, and aPLA profiles. MP-TF (median and (IQR)) in asymptomatic aPLA subjects was 0.09 pg/mL (0.05-0.14) compared to 0.13 pg/mL (0.10-0.17) in APS (p < 0.001). No differences in MP-TF levels were observed between APS subjects with PM, thrombosis, or PM+thrombosis. Similarly, among subjects with either APS or asymptomatic aPLA, MP-TF did not differ in the presence or absence of underlying SLE. Prospective studies will be required to determine if plasma MP-TF activity is causally related to thrombotic or gestational complications in APS.
Keywords: Antiphospholipid syndrome; Microparticle; Pregnancy; Thrombosis; Tissue factor.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Giannakopoulos B, Krilis SA. The pathogenesis of the antiphospholipid syndrome. The New England journal of medicine. 2013;368:1033–1044. - PubMed
-
- Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R, Derksen RH, PGDEG, Koike T, Meroni PL, Reber G, Shoenfeld Y, Tincani A, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG, Krilis SA. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) Journal of thrombosis and haemostasis : JTH. 2006;4:295–306. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz-Irastorza G, Crowther M, Branch W, Khamashta MA. Antiphospholipid syndrome. Lancet. 2010;376:1498–1509. - PubMed
-
- Amengual O, Atsumi T, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR. The role of the tissue factor pathway in the hypercoagulable state in patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Thrombosis and haemostasis. 1998;79:276–281. - PubMed
-
- Atsumi T, Khamashta MA, Amengual O, Hughes GR. Up-regulated tissue factor expression in antiphospholipid syndrome. Thrombosis and haemostasis. 1997;77:222–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

