The advancing clinical impact of molecular imaging in CVD
- PMID: 24332285
- PMCID: PMC3876961
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.09.014
The advancing clinical impact of molecular imaging in CVD
Abstract
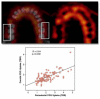
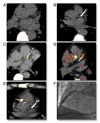
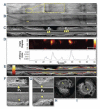
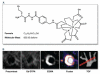
Molecular imaging seeks to unravel critical molecular and cellular events in living subjects by providing complementary biological information to current structural clinical imaging modalities. In recent years, molecular imaging efforts have marched forward into the clinical cardiovascular arena, and are now actively illuminating new biology in a broad range of conditions, including atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, vasculitis, aneurysm, cardiomyopathy, and valvular disease. Development of novel molecular imaging reporters is occurring for many clinical cardiovascular imaging modalities (positron emission tomography, single-photon emission computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging), as well as in translational platforms such as intravascular fluorescence imaging. The ability to image, track, and quantify molecular biomarkers in organs not routinely amenable to biopsy (e.g., the heart and vasculature) open new clinical opportunities to tailor therapeutics based on a cardiovascular disease molecular profile. In addition, molecular imaging is playing an increasing role in atherosclerosis drug development in phase II clinical trials. Here, we present state-of-the-art clinical cardiovascular molecular imaging strategies, and explore promising translational approaches positioned for clinical testing in the near term.
Keywords: (158)Gd-ESMA; (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose; (18)F-sodium fluoride; AS; AT1R; CAC; CEA; CMR; CT; DVT; FDA; FDG; Food and Drug Administration; ICG; LDL; LV; MI; MMP; MRI; NIRF; NaF; OFDI; OTW; PC; PET; RAAS; SUV; TBR; USPIO; aneurysm; angiotensin II type 1 receptor; aortic stenosis; atherosclerosis; cardiac magnetic resonance; carotid endarterectomy; computed tomography; coronary artery calcium; deep vein thrombosis; gadolinium-labeled elastin-specific magnetic resonance contrast agent; heart failure; high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; hsCRP; indocyanine green; left ventricle/ventricular; low-density lipoprotein; magnetic resonance imaging; matrix metalloproteinase; molecular imaging; myocardial infarction; near-infrared fluorescence; optical frequency domain imaging; over-the-wire; perfusion catheter; positron emission tomography; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; standardized uptake value; target-to-background ratio; thrombosis; ultrasmall superparamagnetic particles of iron oxide; valvular disease; vascular injury.
Copyright © 2013 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

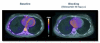
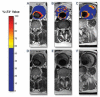
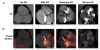
References
-
- Figueroa AL, Subramanian SS, Cury RC, et al. Distribution of inflammation within carotid atherosclerotic plaques with high-risk morphological features: a comparison between positron emission tomography activity, plaque morphology, and histopathology. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;5:69–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

