Incidence of visual improvement in uveitis cases with visual impairment caused by macular edema
- PMID: 24332536
- PMCID: PMC3946576
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.09.023
Incidence of visual improvement in uveitis cases with visual impairment caused by macular edema
Abstract
Purpose: Among cases of visually significant uveitic macular edema (ME), to estimate the incidence of visual improvement and identify predictive factors.
Design: Retrospective cohort study.
Participants: Eyes with uveitis, seen at 5 academic ocular inflammation centers in the United States, for which ME was documented to be currently present and the principal cause of reduced visual acuity (<20/40).
Methods: Data were obtained by standardized chart review.
Main outcome measures: Decrease of ≥ 0.2 base 10 logarithm of visual acuity decimal fraction-equivalent; risk factors for such visual improvement.
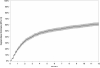
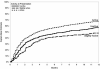
Results: We identified 1510 eyes (of 1077 patients) with visual impairment to a level <20/40 attributed to ME. Most patients were female (67%) and white (76%), and had bilateral uveitis (82%). The estimated 6-month incidence of ≥ 2 lines of visual acuity improvement in affected eyes was 52% (95% confidence interval [CI], 49%-55%). Vision reduced by ME was more likely to improve by 2 lines in eyes initially with poor visual acuity (≤ 20/200; adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 1.5; 95% CI, 1.3-1.7), active uveitis (HR, 1.3; 95% CI, 1.1-1.5), and anterior uveitis as opposed to intermediate (HR, 1.2), posterior (HR, 1.3), or panuveitis (HR, 1.4; overall P = 0.02). During follow-up, reductions in anterior chamber or vitreous cellular activity or in vitreous haze each led to significant improvements in visual outcome (P <0.001 for each). Conversely, snowbanking (HR, 0.7; 95% CI, 0.4-0.99), posterior synechiae (HR, 0.8; 95% CI, 0.6-0.9), and hypotony (HR, 0.2; 95% CI, 0.06-0.5) each were associated with lower incidence of visual improvement with respect to eyes lacking each of these attributes at a given visit.
Conclusions: These results suggest that many, but not all, patients with ME causing low vision in a tertiary care setting will enjoy meaningful visual recovery in response to treatment. Evidence of significant ocular damage from inflammation (posterior synechiae and hypotony) portends a lower incidence of visual recovery. Better control of anterior chamber or vitreous activity is associated with a greater incidence of visual improvement, supporting an aggressive anti-inflammatory treatment approach for ME cases with active inflammation.
Copyright © 2014 American Academy of Ophthalmology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Lardenoye CW, van Kooji B, Rothova A. Impact of macular edema on visual acuity in uveitis. Ophthalmology. 2006;113:1446–9. - PubMed
-
- Malinowski SM, Pulido JS, Folk JC. Long-term visual outcome and complications associated with pars planitis. Ophthalmology. 1993;100:818–24. - PubMed
-
- Yanoff M, Fine BS, Brucker AJ, Eagle RC., Jr Pathology of human cystoid macular edema. Surv Ophthalmol. 1984;28(suppl):505–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

