Impact of pre-stage II hemodynamics and pulmonary artery anatomy on 12-month outcomes in the Pediatric Heart Network Single Ventricle Reconstruction trial
- PMID: 24332668
- PMCID: PMC4053497
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2013.10.057
Impact of pre-stage II hemodynamics and pulmonary artery anatomy on 12-month outcomes in the Pediatric Heart Network Single Ventricle Reconstruction trial
Abstract
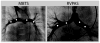
Objective: To compare the interstage cardiac catheterization hemodynamic and angiographic findings between shunt types for the Pediatric Heart Network Single Ventricle Reconstruction trial. The trial, which randomized subjects to a modified Blalock-Taussig shunt (MBTS) or right ventricle-to-pulmonary artery shunt (RVPAS) for the Norwood procedure, demonstrated the RVPAS was associated with a smaller pulmonary artery diameter but superior 12-month transplant-free survival.
Methods: We analyzed the pre-stage II catheterization data for the trial subjects. The hemodynamic variables and shunt and pulmonary angiographic data were compared between shunt types; their association with 12-month transplant-free survival was also evaluated.
Results: Of 549 randomized subjects, 389 underwent pre-stage II catheterization. A smaller size, lower aortic and superior vena cava saturation, and higher ventricular end-diastolic pressure were associated with worse 12-month transplant-free survival. The MBTS group had a lower coronary perfusion pressure (27 vs 32 mm Hg; P<.001) and greater pulmonary blood flow/systemic blood flow ratio (1.1 vs 1.0, P=.009). A greater pulmonary blood flow/systemic blood flow ratio increased the risk of death or transplantation only in the RVPAS group (P=.01). The MBTS group had fewer shunt (14% vs 28%, P=.004) and severe left pulmonary artery (0.7% vs 9.2%, P=.003) stenoses, larger mid-main branch pulmonary artery diameters, and greater Nakata indexes (164 vs 134, P<.001).
Conclusions: Compared with the RVPAS subjects, the MBTS subjects had more hemodynamic abnormalities related to shunt physiology, and the RVPAS subjects had more shunt or pulmonary obstruction of a severe degree and inferior pulmonary artery growth at pre-stage II catheterization. A lower body surface area, greater ventricular end-diastolic pressure, and lower superior vena cava saturation were associated with worse 12-month transplant-free survival.
Copyright © 2014 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Alsoufi B, Bennetts J, Verma S, Caldarone CA. New developments in the treatment of hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Pediatrics. 2007 Jan;119(1):109–17. - PubMed
-
- Ballweg JA, Dominguez TE, Ravishankar C, Kreutzer J, Marino BS, Bird GL, et al. A contemporary comparison of the effect of shunt type in hypoplastic left heart syndrome on the hemodynamics and outcome at stage 2 reconstruction. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007 Aug;134(2):297–303. - PubMed
-
- Tabbutt S, Dominguez TE, Ravishankar C, Marino BS, Gruber PJ, Wernovsky G, et al. Outcomes after the stage I reconstruction comparing the right ventricular to pulmonary artery conduit with the modified Blalock Taussig shunt. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005 Nov;80(5):1582–90. discussion 90–1. - PubMed
-
- Azakie A, Martinez D, Sapru A, Fineman J, Teitel D, Karl TR. Impact of right ventricle to pulmonary artery conduit on outcome of the modified Norwood procedure. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004 May;77(5):1727–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HL068288/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109781/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068279/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068285/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL109737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068269/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068279/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068288/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL109781/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL085057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068269/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068270/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL085057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109778/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL068285/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL068292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

