Iron supplementation does not worsen respiratory health or alter the sputum microbiome in cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 24332997
- PMCID: PMC3972336
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcf.2013.11.004
Iron supplementation does not worsen respiratory health or alter the sputum microbiome in cystic fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Iron supplementation for hypoferremic anemia could potentiate bacterial growth in the cystic fibrosis (CF) lung, but clinical trials testing this hypothesis are lacking.
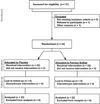
Methods: Twenty-two adults with CF and hypoferremic anemia participated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial of ferrous sulfate 325mg daily for 6weeks. Iron-related hematologic parameters, anthropometric data, sputum iron, Akron Pulmonary Exacerbation Score (PES), and the sputum microbiome were serially assessed. Fixed-effect models were used to describe how ferrous sulfate affected these variables.
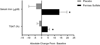
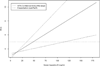
Results: Ferrous sulfate increased serum iron by 22.3% and transferrin saturation (TSAT) by 26.8% from baseline (p<0.05) but did not affect hemoglobin, sputum iron, Akron PES, and the sputum microbiome.
Conclusions: Low-dose ferrous sulfate improved hypoferremia without correcting anemia after 6weeks. We did not observe significant effects on sputum iron, Akron PES, and the sputum microbiome. Although we did not identify untoward health effects of iron supplementation, a larger blinded randomized controlled trial would be needed to fully demonstrate safety.
Keywords: Anemia; Cystic fibrosis; Hepcidin-25; Hypoferremia; Iron; Microbiome.
Copyright © 2013 European Cystic Fibrosis Society. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Regarding the article entitled "Iron supplementation does not worsen respiratory health or alter the sputum microbiome in cystic fibrosis".J Cyst Fibros. 2015 Jan;14(1):158-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 25. J Cyst Fibros. 2015. PMID: 24972893 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fischer R, Simmerlein R, Huber RM, Schiffl H, Lang SM. Lung disease severity, chronic inflammation, iron deficiency, and erythropoietin response in adults with cystic fibrosis. Pediatric pulmonology. 2007;42(12):1193–1197. Epub 2007/10/20. - PubMed
-
- Pond MN, Morton AM, Conway SP. Functional iron deficiency in adults with cystic fibrosis. Respiratory medicine. 1996;90(7):409–413. Epub 1996/08/01. - PubMed
-
- von Drygalski A, Biller J. Anemia in cystic fibrosis: incidence, mechanisms, and association with pulmonary function and vitamin deficiency. Nutrition in clinical practice : official publication of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. 2008;23(5):557–563. Epub 2008/10/14. - PubMed
-
- Wrighting DM, Andrews NC. Iron homeostasis and erythropoiesis. Current topics in developmental biology. 2008;82:141–167. Epub 2008/02/20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

