Typology of alcohol users based on longitudinal patterns of drinking
- PMID: 24333036
- PMCID: PMC3899787
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.11.013
Typology of alcohol users based on longitudinal patterns of drinking
Abstract
Objective: Worldwide, alcohol is the most commonly used psychoactive substance. However, heterogeneity among alcohol users has been widely recognized. This paper presents a typology of alcohol users based on an implementation of idiographic methodology to examine longitudinal daily and cyclic (weekly) patterns of alcohol use at the individual level.
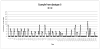
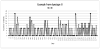
Method: A secondary data analysis was performed on the pre-intervention data from a large randomized control trial. A time series analysis was performed at the individual level, and a dynamic cluster analysis was employed to identify homogenous longitudinal patterns of drinking behavior at the group level. The analysis employed 180 daily observations of alcohol use in a sample of 177 alcohol users.
Results: The first order autocorrelations ranged from -.76 to .72, and seventh order autocorrelations ranged from -.27 to .79. Eight distinct profiles of alcohol users were identified, each characterized by a unique configuration of first and seventh autoregressive terms and longitudinal trajectories of alcohol use. External validity of the profiles confirmed the theoretical relevance of different patterns of alcohol use. Significant differences among the eight subtypes were found on gender, marital status, frequency of drug use, lifetime alcohol dependence, family history of alcohol use and the Short Index of Problems.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that individuals can have very different temporal patterns of drinking behavior. The daily and cyclic patterns of alcohol use may be important for designing tailored interventions for problem drinkers.
Keywords: Dynamic typology; Idiographic research; Longitudinal alcohol use patterns; Time series analysis.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Aalto-Setala T, Marttunen M, Tuulio-Henriksson A, Poikolainen K, Lonnqvist J. Depressive symptoms in adolescence as predictors of early adulthood depressive disorders and maladjustment. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2002;159:1235–1237. - PubMed
-
- Aldenderfer MS, Blashfield RK. Cluster Analysis. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage Publications; 1984.
-
- Aloia MS, Goodwin MS, Velicer WF, Arnedt JT, Zimmerman M, Skrekas J, Harris S, Millman RP. Time Series Analysis of Treatment Adherence Patterns in Individuals with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Annuals of Behavioral Medicine. 2008;36:44–53. - PubMed
-
- Babbin SF, Velicer WF, Aloia M, Kushida C, Berry R. Time series analysis of adherence to treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. Annuals of Behavioral Medicine. 2011;41:S170. (Abstract)
-
- Babor TF, Hofmann M, DelBoca FK, Hesselbrock V, Meyer RE, Dolinsky ZS, et al. Types of alcoholics, I. Evidence for an empirically derived typology based on indicators of vulnerability and severity. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1992;49:599–608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

