A role for hippocampal PSA-NCAM and NMDA-NR2B receptor function in flavonoid-induced spatial memory improvements in young rats
- PMID: 24333331
- PMCID: PMC4062943
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.12.003
A role for hippocampal PSA-NCAM and NMDA-NR2B receptor function in flavonoid-induced spatial memory improvements in young rats
Abstract
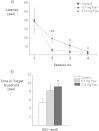
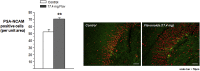
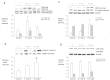
The increase in incidence and prevalence of neurodegenerative diseases highlights the need for a more comprehensive understanding of how food components may affect neural systems. In particular, flavonoids have been recognized as promising agents capable of influencing different aspects of synaptic plasticity resulting in improvements in memory and learning in both animals and humans. Our previous studies highlight the efficacy of flavonoids in reversing memory impairments in aged rats, yet little is known about the effects of these compounds in healthy animals, particularly with respect to the molecular mechanisms by which flavonoids might alter the underlying synaptic modifications responsible for behavioral changes. We demonstrate that a 3-week intervention with two dietary doses of flavonoids (Dose I: 8.7 mg/day and Dose II: 17.4 mg/day) facilitates spatial memory acquisition and consolidation (24 recall) (p < 0.05) in young healthy rats. We show for the first time that these behavioral improvements are linked to increased levels in the polysialylated form of the neural adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM) in the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus, which is known to be required for the establishment of durable memories. We observed parallel increases in hippocampal NMDA receptors containing the NR2B subunit for both 8.7 mg/day (p < 0.05) and 17.4 mg/day (p < 0.001) doses, suggesting an enhancement of glutamate signaling following flavonoid intervention. This is further strengthened by the simultaneous modulation of hippocampal ERK/CREB/BDNF signaling and the activation of the Akt/mTOR/Arc pathway, which are crucial in inducing changes in the strength of hippocampal synaptic connections that underlie learning. Collectively, the present data supports a new role for PSA-NCAM and NMDA-NR2B receptor on flavonoid-induced improvements in learning and memory, contributing further to the growing body of evidence suggesting beneficial effects of flavonoids in cognition and brain health.
Keywords: BDNF; Flavonoid; Hippocampus; Learning; Memory; NMDR2B; PSA-NCAM.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhanced NMDA receptor pathway and glutamate transmission in the hippocampal dentate gyrus mediate the spatial learning and memory impairment of obese rats.Pflugers Arch. 2024 May;476(5):821-831. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-02924-1. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Pflugers Arch. 2024. PMID: 38416255 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of CB1 cannabinoid receptors impairs memory consolidation and hippocampal polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule expression in contextual fear conditioning.Neuroscience. 2009 Feb 18;158(4):1708-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.11.037. Epub 2008 Dec 3. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19110037
-
Acute activation of CB1 cannabinoid receptors transiently decreases PSA-NCAM expression in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus.Brain Res. 2007 May 7;1148:43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.02.014. Epub 2007 Feb 17. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17355876
-
PSA-NCAM: synaptic functions mediated by its interactions with proteoglycans and glutamate receptors.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;44(4):591-5. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.01.008. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22300986 Review.
-
Synaptic plasticity and neuroprotection: The molecular impact of flavonoids on neurodegenerative disease progression.Neuroscience. 2025 Mar 17;569:161-183. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2025.02.007. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Neuroscience. 2025. PMID: 39922366 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Nigella sativa and Its Active Constituents in Learning and Memory.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:6075679. doi: 10.1155/2016/6075679. Epub 2016 Feb 28. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27022403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exercise but not (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate or β-alanine enhances physical fitness, brain plasticity, and behavioral performance in mice.Physiol Behav. 2015 Jun 1;145:29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.03.023. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Physiol Behav. 2015. PMID: 25797079 Free PMC article.
-
Acquisition-dependent modulation of hippocampal neural cell adhesion molecules by associative motor learning.Front Neuroanat. 2022 Dec 21;16:1082701. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2022.1082701. eCollection 2022. Front Neuroanat. 2022. PMID: 36620194 Free PMC article.
-
Anthocyanins Promote Learning through Modulation of Synaptic Plasticity Related Proteins in an Animal Model of Ageing.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jul 31;10(8):1235. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081235. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439483 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Compounds and Traditional Herbal Medicine: Promising Approaches for the Treatment of Dementia.Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis. 2021 Apr 12;11:1-14. doi: 10.2147/DNND.S299589. eCollection 2021. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis. 2021. PMID: 33880073 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aimone J.B., Wiles J., Gage F.H. Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nat. Neurosci. 2006;9(6):723–727. - PubMed
-
- Aonurm-Helm A., Zharkovsky T., Jurgenson M., Kalda A., Zharkovsky A. Dysregulated CREB signaling pathway in the brain of neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM)-deficient mice. Brain Res. 2008;1243:104–112. - PubMed
-
- Becker C.G., Artola A., Gerardy-Schahn R., Becker T., Welzl H., Schachner M. The polysialic acid modification of the neural cell adhesion molecule is involved in spatial learning and hippocampal long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. Res. 1996;45(2):143–152. - PubMed
-
- Bekinschtein P., Katche C., Slipczuk L.N., Igaz L.M., Cammarota M., Izquierdo I. mTOR signaling in the hippocampus is necessary for memory formation. Neurobiol. Learn. Memory. 2007;87(2):303–307. - PubMed
-
- Benson D.L., Schnapp L.M., Shapiro L., Huntley G.W. Making memories stick: cell-adhesion molecules in synaptic plasticity. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10(11):473–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

