Sleep deprivation impairs performance in the 5-choice continuous performance test: similarities between humans and mice
- PMID: 24333377
- PMCID: PMC3937379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.12.003
Sleep deprivation impairs performance in the 5-choice continuous performance test: similarities between humans and mice
Abstract
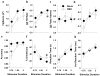
Several groups undergo extended periods without sleep due to working conditions or mental illness. Such sleep deprivation (SD) can deleteriously affect attentional processes and disrupt work and family functioning. Understanding the biological underpinnings of SD effects may assist in developing sleep therapies and cognitive enhancers. Utilizing cross-species tests of attentional processing in humans and rodents would aid in mechanistic studies examining SD-induced inattention. We assessed the effects of 36h of: (1) Total SD (TSD) in healthy male and female humans (n=50); and (2) REM SD (RSD) in male C57BL/6 mice (n=26) on performance in the cross-species 5-choice continuous performance test (5C-CPT). The 5C-CPT includes target trials on which subjects were required to respond and non-target trials on which subjects were required to inhibit from responding. TSD-induced effects on human psychomotor vigilance test (PVT) were also examined. Effects of SD were also examined on mice split into good and poor performance groups based on pre-deprivation scores. In the human 5C-CPT, TSD decreased hit rate and vigilance with trend-level effects on accuracy. In the PVT, TSD slowed response times and increased lapses. In the mouse 5C-CPT, RSD reduced accuracy and hit rate with trend-level effects on vigilance, primarily in good performers. In conclusion, SD induced impaired 5C-CPT performance in both humans and mice and validates the 5C-CPT as a cross-species translational task. The 5C-CPT can be used to examine mechanisms underlying SD-induced deficits in vigilance and assist in testing putative cognitive enhancers.
Keywords: 5-Choice Continuous Performance Test; 5-Choice Serial Reaction Time Task; 5C-CPT; 5CSRTT; Attention; Bipolar disorder; CPT; CR; Correct rejection; FA; FA rate; FAR; False alarm; HR; Hit rate; ITI; Inter-trial interval; PVT; Psychomotor Vigilance Test; Psychomotor vigilance test; REM; REM sleep deprivation; RI; RSD; RT; Rapid eye movement; Reaction time; Responsivity index; SD; Sleep deprivation; TSD; Total sleep deprivation; Vigilance; vRT; variable RT.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures

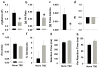

References
-
- Killgore WD. Effects of sleep deprivation on cognition. Prog Brain Res. 2010;185:105–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

