Analysis of 27 vascular-related proteins reveals that NT-proBNP is a potential biomarker for Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: a pilot-study
- PMID: 24333505
- PMCID: PMC4312837
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.12.001
Analysis of 27 vascular-related proteins reveals that NT-proBNP is a potential biomarker for Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: a pilot-study
Abstract
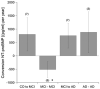
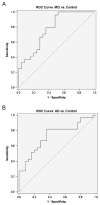
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a severe neurodegenerative disease. Cerebrovascular changes often accompany AD-related pathology. Despite a considerable progress in the diagnostic accuracy of AD, no blood biomarkers have been established so far. The aim of the present study was to search for changes in plasma levels of 27 vascular-related proteins of healthy controls, patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and AD. In a sample of 80 participants we showed that out of these 27 proteins, six proteins were slightly changed (up to 1.5×) in AD (alpha2-macroglobulin, apolipoprotein-A1, plasminogen activator inhibitor, RAGE, Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinases-1 and Trombospondin-2) and one marker (serum amyloid A) was enhanced up to 6× but with a very high variance. However, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) was significantly enhanced both in MCI and AD patients (1.9×). In a second analysis of a sample of 110 subjects including younger healthy controls, we confirmed that NT-proBNP has the potential to be a stable candidate protein for both diagnosis and AD disease progression.
Keywords: Alzheimer; Biomarker; Diagnosis; Mild cognitive impairment; Multiplex ELISA; NT-proBNP; Plasma.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
N-Terminal Pro-B Type Natriuretic Peptide is Associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment in the General Population.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;55(1):359-369. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160635. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 27636851
-
N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and Risk of Future Cognitive Impairment in the REGARDS Cohort.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016 Sep 6;54(2):497-503. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160328. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 27567834
-
Decreasing body mass index is associated with cerebrospinal fluid markers of Alzheimer's pathology in MCI and mild dementia.Exp Gerontol. 2017 Dec 15;100:45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.10.013. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Exp Gerontol. 2017. PMID: 29054536
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 as an early potential diagnostic marker for Alzheimer's disease.Exp Gerontol. 2014 Dec;60:87-91. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2014.10.004. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Exp Gerontol. 2014. PMID: 25304332
-
Evaluation of the diagnostic value of peripheral BDNF levels for Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: results of a meta-analysis.Int J Neurosci. 2020 Mar;130(3):218-230. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2019.1667794. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Int J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31518516 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of inflammatory and vascular markers associated with mild cognitive impairment.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Apr 30;11(8):2403-2419. doi: 10.18632/aging.101924. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31039131 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of Serum Amyloid A Proteins with the Blood-Brain Barrier: Implications for Central Nervous System Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 15;25(12):6607. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126607. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential fluid biomarkers for pathological brain changes in Alzheimer's disease: Implication for the screening of cognitive frailty.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Oct;14(4):3184-98. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5618. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27511317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic review of amyloid-beta clearance proteins from the brain to the periphery: implications for Alzheimer's disease diagnosis and therapeutic targets.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Dec 1;20(12):3574-3590. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00865. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39820231 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein A1, the neglected relative of Apolipoprotein E and its potential role in Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Nov;16(11):2141-2148. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.310669. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33818485 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bayes-Genis A. Plasma NT-proBNP: a new biomarker for diagnosis and monitoring of congestive heart failure (CHF) Timely Top. Med. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006;10:E10. - PubMed
-
- Bionda C, Bergerot C, Ardail D, Rodriguez-Lafrasse C, Rousson R. Plasma BNP and NT-proBNP assays by automated immunoanalyzers: analytical and clinical study. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2006;36:299–306. - PubMed
-
- Blasko I, Lederer W, Oberbauer H, Walch T, Kemmler G, Hinterhuber H, Marksteiner J, Humpel C. Measurement of thirteen biological markers in CSF of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2006;21:9–15. - PubMed
-
- Blennow K. CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: use in erarly diagnosis and evaluation of drug treatment. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2005;5:661–672. - PubMed
-
- Borroni B, Volpi R, Martini G, Del Bono R, Archetti S, Colciaghi F, Akkawi NM, Di Luca M, Romanelli G, Caimi L, Padovani A. Peripheral blood abnormalities in Alzheimer disease: evidence for early endothelial dysfunction. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2002;16:150–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

