The regulation of RhoA at focal adhesions by StarD13 is important for astrocytoma cell motility
- PMID: 24333506
- PMCID: PMC4297755
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.11.023
The regulation of RhoA at focal adhesions by StarD13 is important for astrocytoma cell motility
Abstract
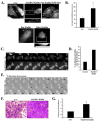
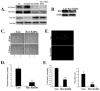
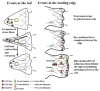
Malignant astrocytomas are highly invasive into adjacent and distant regions of the normal brain. Rho GTPases are small monomeric G proteins that play important roles in cytoskeleton rearrangement, cell motility, and tumor invasion. In the present study, we show that the knock down of StarD13, a GTPase activating protein (GAP) for RhoA and Cdc42, inhibits astrocytoma cell migration through modulating focal adhesion dynamics and cell adhesion. This effect is mediated by the resulting constitutive activation of RhoA and the subsequent indirect inhibition of Rac. Using Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence (TIRF)-based Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET), we show that RhoA activity localizes with focal adhesions at the basal surface of astrocytoma cells. Moreover, the knock down of StarD13 inhibits the cycling of RhoA activation at the rear edge of cells, which makes them defective in retracting their tail. This study highlights the importance of the regulation of RhoA activity in focal adhesions of astrocytoma cells and establishes StarD13 as a GAP playing a major role in this process.
Keywords: Astrocytoma; Cell motility; Rac; RhoA; StarD13.
© 2013 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
StarD13: a potential star target for tumor therapeutics.Hum Cell. 2020 Jul;33(3):437-443. doi: 10.1007/s13577-020-00358-2. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Hum Cell. 2020. PMID: 32274657 Review.
-
Effect of StarD13 on colorectal cancer proliferation, motility and invasion.Oncol Rep. 2014 Jan;31(1):505-15. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2861. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24253896
-
DLC2/StarD13 plays a role of a tumor suppressor in astrocytoma.Oncol Rep. 2012 Aug;28(2):511-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1819. Epub 2012 May 17. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22614672
-
StarD13 differentially regulates migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells.Hum Cell. 2021 Mar;34(2):607-623. doi: 10.1007/s13577-020-00479-8. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 33420961
-
Dynamic functions of RhoA in tumor cell migration and invasion.Small GTPases. 2013 Jul-Sep;4(3):141-7. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.25131. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Small GTPases. 2013. PMID: 24025634 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
StarD13 negatively regulates invadopodia formation and invasion in high-grade serous (HGS) ovarian adenocarcinoma cells by inhibiting Cdc42.Eur J Cell Biol. 2022 Jan;101(1):151197. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2021.151197. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Eur J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34958986 Free PMC article.
-
StarD13: a potential star target for tumor therapeutics.Hum Cell. 2020 Jul;33(3):437-443. doi: 10.1007/s13577-020-00358-2. Epub 2020 Apr 9. Hum Cell. 2020. PMID: 32274657 Review.
-
Resveratrol suppresses human glioblastoma cell migration and invasion via activation of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2016 Jan;11(1):484-490. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3888. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26870238 Free PMC article.
-
The Cytoskeleton-A Complex Interacting Meshwork.Cells. 2019 Apr 18;8(4):362. doi: 10.3390/cells8040362. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31003495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-125b promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting STARD13 and NEU1.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):12141-12151. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5094-y. Epub 2016 May 24. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27220320
References
-
- CBTRUS. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2004–2007. Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States; Hinsdale, IL: 2011.
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:492–507. - PubMed
-
- Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME, Westphal M. Cost of migration: invasion of malignant gliomas and implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1624–1636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

