Expression of LIM-homeodomain transcription factors in the developing and mature mouse retina
- PMID: 24333658
- PMCID: PMC3921069
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gep.2013.12.001
Expression of LIM-homeodomain transcription factors in the developing and mature mouse retina
Abstract
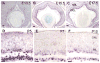
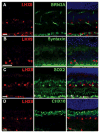
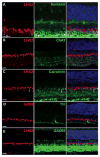
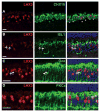
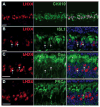
LIM-homeodomain (LIM-HD) transcription factors have been extensively studied for their role in the development of the central nervous system. Their function is key to several developmental events like cell proliferation, differentiation and subtype specification. However, their roles in retinal neurogenesis remain largely unknown. Here we report a detailed expression study of LIM-HD transcription factors LHX9 and LHX2, LHX3 and LHX4, and LHX6 in the developing and mature mouse retina using immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization techniques. We show that LHX9 is expressed during the early stages of development in the retinal ganglion cell layer and the inner nuclear layer. We also show that LHX9 is expressed in a subset of amacrine cells in the adult retina. LHX2 is known to be expressed in retinal progenitor cells during development and in Müller glial cells and a subset of amacrine cells in the adult retina. We found that the LHX2 subset of amacrine cells is not cholinergic and that a very few of LHX2 amacrine cells express calretinin. LHX3 and LHX4 are expressed in a subset of bipolar cells in the adult retina. LHX6 is expressed in cells in the ganglion cell layer and the neuroblast layer starting at embryonic stage 13.5 (E13.5) and continues to be expressed in cells in the ganglion cell layer and inner nuclear layer, postnatally, suggesting its likely expression in amacrine cells or a subset thereof. Taken together, our comprehensive assay of expression patterns of LIM-HD transcription factors during mouse retinal development will help further studies elucidating their biological functions in the differentiation of retinal cell subtypes.
Keywords: LIM-homeodomain; Lhx genes; Retinal development; Retinogenesis; Transcription factors.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abellan A, Legaz I, et al. Olfactory and amygdalar structures of the chicken ventral pallium based on the combinatorial expression patterns of LIM and other developmental regulatory genes. J Comp Neurol. 2009;516(3):166–186. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson-Leadbeater K, Bertolesi GE, et al. FGF receptor dependent regulation of Lhx9 expression in the developing nervous system. Dev Dyn. 2009;238(2):367–375. - PubMed
-
- Bach I. The LIM domain: regulation by association. Mech Dev. 2000;91(1–2):5–17. - PubMed
-
- Bertuzzi S, Porter FD, et al. Characterization of Lhx9, a novel LIM/homeobox gene expressed by the pioneer neurons in the mouse cerebral cortex. Mech Dev. 1999;81(1–2):193–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

