Flk2/Flt3 promotes both myeloid and lymphoid development by expanding non-self-renewing multipotent hematopoietic progenitor cells
- PMID: 24333663
- PMCID: PMC4047989
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2013.11.013
Flk2/Flt3 promotes both myeloid and lymphoid development by expanding non-self-renewing multipotent hematopoietic progenitor cells
Abstract
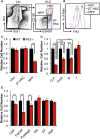
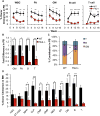
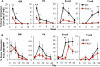
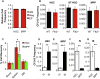
Defining differentiation pathways is central to understanding the pathogenesis of hematopoietic disorders, including leukemia. The function of the receptor tyrosine kinase Flk2 (Flt3) in promoting myeloid development remains poorly defined, despite being commonly mutated in acute myeloid leukemia. We investigated the effect of Flk2 deficiency on myelopoiesis, focusing on specification of progenitors between HSC and mature cells. We provide evidence that Flk2 is critical for proliferative expansion of multipotent progenitors that are common precursors for all lymphoid and myeloid lineages, including megakaryocyte/erythroid (MegE) cells. Flk2 deficiency impaired the generation of both lymphoid and myeloid progenitors by abrogating propagation of their common upstream precursor. At steady state, downstream compensatory mechanisms masked the effect of Flk2 deficiency on mature myeloid output, whereas transplantation of purified progenitors revealed impaired generation of all mature lineages. Flk2 deficiency did not affect lineage choice, thus dissociating the role of Flk2 in promoting cell expansion and regulating cell fate. Surprisingly, despite impairing myeloid development, Flk2 deficiency afforded protection against myeloablative insult. This survival advantage was attributed to reduced cell cycling and proliferation of progenitors in Flk2-deficient mice. Our data support the existence of a common Flk2(+) intermediate for all hematopoietic lineages and provide insight into how activating Flk2 mutations promote hematopoietic malignancy by non-Flk2-expressing myeloid cells.
Copyright © 2014 ISEH - Society for Hematology and Stem Cells. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No financial interest/relationships with financial interest relating to the topic of this article have been declared.
Figures
References
-
- Adolfsson J, Mansson R, Buza-Vidas N, et al. Identification of Flt3+ lympho-myeloid stem cells lacking erythro-megakaryocytic potential a revised road map for adult blood lineage commitment. Cell. 2005;121:295–306. - PubMed
-
- Hunte BE, Hudak S, Campbell D, Xu Y, Rennick D. flk2/flt3 ligand is a potent cofactor for the growth of primitive B cell progenitors. J Immunol. 1996;156:489–496. - PubMed
-
- Hudak S, Hunte B, Culpepper J, et al. FLT3/FLK2 ligand promotes the growth of murine stem cells and the expansion of colony-forming cells and spleen colony-forming units. Blood. 1995;85:2747–2755. - PubMed
-
- Hirayama F, Lyman SD, Clark SC, Ogawa M. The flt3 ligand supports proliferation of lymphohematopoietic progenitors and early B-lymphoid progenitors. Blood. 1995;85:1762–1768. - PubMed
-
- Adolfsson J, Borge OJ, Bryder D, et al. Upregulation of Flt3 expression within the bone marrow Lin(−)Sca1(+)c-kit(+) stem cell compartment is accompanied by loss of self-renewal capacity. Immunity. 2001;15:659–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

