TGL-mediated lipolysis in Manduca sexta fat body: possible roles for lipoamide-dehydrogenase (LipDH) and high-density lipophorin (HDLp)
- PMID: 24333838
- PMCID: PMC3932539
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.12.001
TGL-mediated lipolysis in Manduca sexta fat body: possible roles for lipoamide-dehydrogenase (LipDH) and high-density lipophorin (HDLp)
Abstract
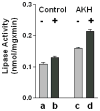
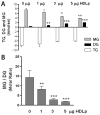
Triglyceride-lipase (TGL) is a major fat body lipase in Manduca sexta. The knowledge of how TGL activity is regulated is very limited. A WWE domain, presumably involved in protein-protein interactions, has been previously identified in the N-terminal region of TGL. In this study, we searched for proteins partners that interact with the N-terminal region of TGL. Thirteen proteins were identified by mass spectrometry, and the interaction with four of these proteins was confirmed by immunoblot. The oxidoreductase lipoamide-dehydrogenase (LipDH) and the apolipoprotein components of the lipid transporter, HDLp, were among these proteins. LipDH is the common component of the mitochondrial α-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes whereas HDLp occurs in the hemolymph. However, subcellular fractionation demonstrated that these two proteins are relatively abundant in the soluble fraction of fat body adipocytes. The cofactor lipoate found in typical LipDH substrates was not detected in TGL. However, TGL proved to have critical thiol groups. Additional studies with inhibitors are consistent with the notion that LipDH acting as a diaphorase could preserve the activity of TGL by controlling the redox state of thiol groups. On the other hand, when TG hydrolase activity of TGL was assayed in the presence of HDLp, the production of diacylglycerol (DG) increased. TGL-HDLp interaction could drive the intracellular transport of DG. TGL may be directly involved in the lipoprotein assembly and loading with DG, a process that occurs in the fat body and is essential for insects to mobilize fatty acids. Overall the study suggests that TGL occurs as a multi-protein complex supported by interactions through the WWE domain.
Keywords: Diacylglycerol; Fat body; Lipoamide dehydrogenase; Manduca sexta; Redox; Triglyceride lipase; WWE-domain.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
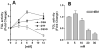
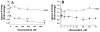
Similar articles
-
Mobilization of lipid stores in Manduca sexta: cDNA cloning and developmental expression of fat body triglyceride lipase, TGL.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Feb;40(2):91-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2009.12.008. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20060045 Free PMC article.
-
Role of diacylglycerol and apolipophorin-III in regulation of physiochemical properties of the lipophorin surface: metabolic implications.Biochemistry. 1996 Apr 23;35(16):5191-8. doi: 10.1021/bi952794d. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8611503
-
Lipid transfer from insect fat body to lipophorin: comparison between a mosquito triacylglycerol-rich lipophorin and a sphinx moth diacylglycerol-rich lipophorin.J Lipid Res. 1996 May;37(5):1144-52. J Lipid Res. 1996. PMID: 8725165
-
Alternative lipid mobilization: the insect shuttle system.Mol Cell Biochem. 2002 Oct;239(1-2):113-9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12479576 Review.
-
Circulatory lipid transport: lipoprotein assembly and function from an evolutionary perspective.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Jun;326(1-2):105-19. doi: 10.1007/s11010-008-0011-3. Epub 2009 Jan 8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19130182 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid Droplets as Signaling Platforms Linking Metabolic and Cellular Functions.Lipid Insights. 2014;7:7-16. doi: 10.4137/LPI.S11128. Lipid Insights. 2014. PMID: 25221429 Free PMC article.
-
Lipase Activity in the Larval Midgut of Rhynchophorus palmarum: Biochemical Characterization and the Effects of Reducing Agents.Insects. 2017 Sep 13;8(3):100. doi: 10.3390/insects8030100. Insects. 2017. PMID: 28902170 Free PMC article.
-
Insect Lipids as Novel Source for Future Applications: Chemical Composition and Industry Applications-A Comprehensive Review.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jul 20;13(7):e70553. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70553. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40688597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replacement of fish meal with cottonseed protein concentrate in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis): Nutrient digestibility, growth performance, free amino acid profile, and expression of genes related to nutrient metabolism.Anim Nutr. 2024 Feb 12;17:447-462. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.02.001. eCollection 2024 Jun. Anim Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38846720 Free PMC article.
-
β-ATPase of the Insect Panstrongylus megistus: Cloning, Bioinformatics Analysis, and Study of Its Interaction With Lipophorin.Proteins. 2025 Sep;93(9):1603-1612. doi: 10.1002/prot.26830. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Proteins. 2025. PMID: 40265662
References
-
- Ålin P, Danielson UH, Mannervik B. 4-Hydroxyalk-2-enals are substrates for glutathione transferase. FEBS Lett. 1985;179:267–270. - PubMed
-
- Aravind L. The WWE domain: a common interaction module in protein ubiquitination and ADP ribosylation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:273–275. - PubMed
-
- Argyrou A, Blanchard JS. Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoamide dehydrogenase is encoded by Rv0462 and not by the lpdA or lpdB genes. Biochemistry. 2001;40:11353–11363. - PubMed
-
- Arrese EL, Flowers MT, Gazard JL, Wells MA. Calcium and cAMP are second messengers in the adipokinetic hormone-induced lipolysis of triacylglycerols in Manduca sexta fat body. J Lipid Res. 1999;40:556–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

