Addition of nitazoxanide to PEG-IFN and ribavirin to improve HCV treatment response in HIV-1 and HCV genotype 1 coinfected persons naïve to HCV therapy: results of the ACTG A5269 trial
- PMID: 24334180
- PMCID: PMC4113390
- DOI: 10.1310/hct1406-274
Addition of nitazoxanide to PEG-IFN and ribavirin to improve HCV treatment response in HIV-1 and HCV genotype 1 coinfected persons naïve to HCV therapy: results of the ACTG A5269 trial
Abstract
Background: We hypothesized that nitazoxanide (NTZ) added to pegylated interferon alfa-2a (PEG-IFN) and weight-based ribavirin (WBR) would improve hepatitis C virus (HCV) virologic responses in HCV treatment-naïve HIV-1/HCV genotype 1 coinfected persons.
Methods: Prospective, single-arm study in which subjects received 4-week lead-in (NTZ 500 mg twice daily) followed by 48 weeks of NTZ, PEG-IFN, and WBR. We compared the HCV virologic responses of these subjects to historical controls from the completed ACTG study A5178 who received PEG-IFN and WBR and had similar subject characteristics. Primary endpoints were early virologic response and complete early virologic response (EVR and cEVR).
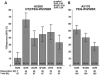
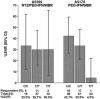
Results: Among 67 subjects (78% male; 48% Black; median age, 50 years), EVR was achieved in 65.7% (90% CI, 55.0%-75.3%), cEVR in 38.8% (28.8%-49.6%). and SVR in 32.8% (23.4%-43.5%). EVR was higher with NTZ (51.4% in A5178; P = .03), but the sustained virologic response (SVR) proportion was similar (27.3% in A5178; P = .24). In contrast to A5178, SVR was similar across IL28B genotypes. Overall, NTZ was safe and well-tolerated.
Conclusion: Whereas EVR proportion improved significantly in this pilot study, the addition of NTZ to PEG-IFN/WBR did not significantly improve SVR compared to historical controls. NTZ may be associated with an attenuation of the effect of IL28B on HCV treatment response.
Keywords: HIV; genotype 1; hepatitis C; nitazoxanide; pegylated interferon; ribavirin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Korba BE, Montero A, Farrar K, et al. Nitazoxanide, tizoxanide and other thiazolides are potent inhibitors of hepatitis B and hepatitis C replication. Antivir Res. 2008;77:56–63. - PubMed
-
- Rossignol JF, Elfert A, Keeffe EB. Treatment of chronic hepatitis C using a 4-week lead-in with nitazoxanide before peginterferon plus nitazoxanide. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;44(7):504–509. - PubMed
-
- Rossignol JF, Elfert A, El-Gohary Y, Keeffe EB. Improved virologic response in chronic hepatitis C genotype 4 treated with nitazoxanide, peginterferon, and ribavirin. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(3):856–862. - PubMed
-
- Rossignol JF. Nitazoxanide in the treatment of acquired immune deficiency syndrome-related cryptosporidiosis: Results of the United States compassionate use program in 365 patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24(5):887–894. - PubMed
-
- Elazar M, Liu M, McKenna SA, et al. The anti-hepatitis C agent nitazoxanide induces phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha via protein kinase activated by double-stranded RNA activation. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(5):1827–1835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1-TR00058/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024996/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069470/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025747/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069419/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069502/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5 UL1 RR021456-07/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012879/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI069556/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI069053/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069419/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069556/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069534/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01 AI069470-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069415/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000058/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1-UO1-AI069503/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069412/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 7UM1AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR 025747/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069496/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069556/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5UM1 AI069415-06/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5UM1 AI06953-07/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069511/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR 024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01- A1069472/PHS HHS/United States
- U01 AI069503/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30AI27767-24/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI069511-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5UO1 AI069502-06/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069419/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000457/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-096497/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069452/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR024996/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
