Rat uterine oxytocin receptor and estrogen receptor α and β mRNA levels are regulated by estrogen through multiple estrogen receptors
- PMID: 24334513
- PMCID: PMC3963296
- DOI: 10.1262/jrd.2012-139
Rat uterine oxytocin receptor and estrogen receptor α and β mRNA levels are regulated by estrogen through multiple estrogen receptors
Abstract
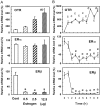
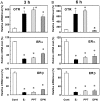
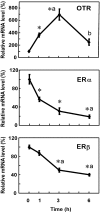
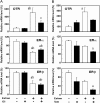
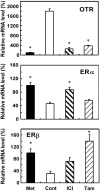
Estrogen action is mediated through several types of receptors (ERs), such as ERα, ERβ and putative membrane ERs. Oxytocin receptor (OTR) and ER expression levels in the rat uterus are regulated by estrogen; however, which types of ERs are involved has not been elucidated. This study examined OTR, ERα and ERβ levels in ovariectomized rats treated with 17β-estradiol (E2), an ERα agonist (PPT), an ERβ agonist (DPN) or estren (Es). E2 and PPT increased OTR mRNA levels and decreased ERα and ERβ mRNA levels 3 and 6 h posttreatment. DPN decreased ERα and ERβ mRNA levels at 3 and 6 h, while OTR mRNA levels increased at 3 h and decreased at 6 h. OTR mRNA levels increased 3 h after the Es treatment and then declined until 6 h. ERα and ERβ mRNA levels decreased by 3 h and remained low until 6 h posttreatment with Es. The ER antagonist ICI182,780 (ICI) suppressed the increases in OTR mRNA levels induced 3 h after the Es treatment. However, ICI and tamoxifen (Tam) had no significant effect on ERα and ERβ mRNA levels in the Es-treated or vehicle-treated group. In intact rats, proestrus-associated increases in OTR mRNA levels were antagonized by both ICI and Tam. However, decreases in ERα and ERβ mRNA levels were not antagonized by Tam and ICI, respectively. Therefore, uterine OTR gene expression is upregulated by estrogen through the classical nuclear (or non-nuclear) ERs, ERα and ERβ, while the levels of these ERs are downregulated by estrogen through multiple pathways including Es-sensitive nonclassical ERs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential regulation of estrogen receptor alpha and beta mRNAs in the rat uterus during pregnancy and labor: possible involvement of estrogen receptors in oxytocin receptor regulation.Endocr J. 2003 Oct;50(5):579-87. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.50.579. Endocr J. 2003. PMID: 14614214
-
Regulation of estrogen receptor (ER) isoform messenger RNA expression by different ER ligands in female rat pituitary.Biol Reprod. 2004 Mar;70(3):671-8. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.021378. Epub 2003 Nov 12. Biol Reprod. 2004. PMID: 14613904
-
Estrogen receptor-beta agonist diarylpropionitrile counteracts the estrogenic activity of estrogen receptor-alpha agonist propylpyrazole-triol in the mammary gland of ovariectomized Sprague Dawley rats.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 May;130(1-2):26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.12.018. Epub 2012 Jan 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22266284
-
Contribution of estrogen receptors alpha and beta to the effects of estradiol in the brain.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008 Feb;108(3-5):327-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.09.011. Epub 2007 Sep 7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 17936613 Review.
-
No detectable changes in anxiety-related and locomotor behaviors in adult ovariectomized female rats exposed to estradiol, the ERβ agonist DPN or the ERα agonist PPT.Horm Behav. 2023 Jun;152:105363. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2023.105363. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Horm Behav. 2023. PMID: 37087765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Beta-Estradiol Regulates Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels and Estrogen Receptors in Telocytes from Human Myometrium.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 9;19(5):1413. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051413. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29747396 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal influences in migraine - interactions of oestrogen, oxytocin and CGRP.Nat Rev Neurol. 2021 Oct;17(10):621-633. doi: 10.1038/s41582-021-00544-2. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34545218 Review.
-
Maca extracts and estrogen replacement therapy in ovariectomized rats exposed at high altitude.Reprod Med Biol. 2020 Nov 11;20(1):88-95. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12357. eCollection 2021 Jan. Reprod Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 33488288 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of estradiol regulation of orexin neurons: a novel mechanism in excessive ventilatory response to CO2 inhalation in a female rat model of panic disorder.Transl Psychiatry. 2020 Nov 10;10(1):394. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-01076-x. Transl Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33173029 Free PMC article.
-
The neurobiology of parenting and infant-evoked aggression.Physiol Rev. 2025 Jan 1;105(1):315-381. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00036.2023. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Physiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39146250 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fuchs A-R, Periyasamy S, Alexandrroa M, Soloff MS. Correlation between oxytocin receptor concentration and responsiveness to oxytocin in pregnant rat myometrium: Effects of ovarian steroids. Endocrinology 1983; 113: 742–749 - PubMed
-
- Soloff MS, Alexandrova M, Fernstrom MJ. Oxytocin receptors: triggers for parturition and lactation? Science 1979; 204: 1313–1315 - PubMed
-
- Fuchs AR, Fuchs F, Husslein P, Soloff MS. Oxytocin receptors in the human uterus during pregnancy and parturition. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1984; 150: 734–741 - PubMed
-
- Maggi M, Genazzani AD, Giannini S, Torrisi C, Baldi E, di Tomaso M, Munson PJ, Rodbard D, Serio M. Vasopressin and oxytocin receptors in vagina, myometrium, and oviduct of rabbits. Endocrinology 1988; 122: 2970–2980 - PubMed
-
- Maggi M, Peri A, Giannini S, Fantoni G, Guardabasso V, Serio M. Oxytocin and V1 vasopressin receptors in rabbit endometrium during pregnancy. J Reprod Fertil 1991; 91: 575–581 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

