The effect of illicit financial flows on time to reach the fourth Millennium Development Goal in Sub-Saharan Africa: a quantitative analysis
- PMID: 24334911
- PMCID: PMC4109330
- DOI: 10.1177/0141076813514575
The effect of illicit financial flows on time to reach the fourth Millennium Development Goal in Sub-Saharan Africa: a quantitative analysis
Abstract
Objectives: This paper sets out to estimate the cost of illicit financial flows (IFF) in terms of the amount of time it could take to reach the fourth Millennium Development Goal (MDG) in 34 African countries.
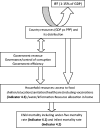
Design: We have calculated the percentage increase in gross domestic product (GDP) if IFFs were curtailed using IFF/GDP ratios. We applied the income (GDP) elasticity of child mortality to the increase in GDP to estimate the reduction in time to reach the fourth MDG in 34 African countries.
Participants: children aged under five years.
Settings: 34 countries in SSA.
Main outcome measures: Reduction in time to reach the first indicator of the fourth MDG, under-five mortality rate in the absence of IFF.
Results: We found that in the 34 SSA countries, six countries will achieve their fourth MDG target at the current rates of decline. In the absence of IFF, 16 countries would reach their fourth MDG target by 2015 and there would be large reductions for all other countries.
Conclusions: This drain on development is facilitated by financial secrecy in other jurisdictions. Rich and poor countries alike must stem the haemorrhage of IFF by taking decisive steps towards improving financial transparency.
Keywords: child mortality; illicit financial flows; millennium development goals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An analysis of the potential for achieving the fourth millennium development goal in SSA with domestic resources.Global Health. 2015 Feb 25;11:8. doi: 10.1186/s12992-015-0092-1. Global Health. 2015. PMID: 25885642 Free PMC article.
-
Social costs of illicit financial flows in low- and middle-income countries: the case of infant vaccination coverage.Health Policy Plan. 2018 Mar 1;33(2):224-236. doi: 10.1093/heapol/czx170. Health Policy Plan. 2018. PMID: 29237018
-
The impact of the worldwide Millennium Development Goals campaign on maternal and under-five child mortality reduction: 'Where did the worldwide campaign work most effectively?'.Glob Health Action. 2017;10(1):1267961. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2017.1267961. Glob Health Action. 2017. PMID: 28168932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drivers of inequality in Millennium Development Goal progress: a statistical analysis.PLoS Med. 2010 Mar 2;7(3):e1000241. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000241. PLoS Med. 2010. PMID: 20209000 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of breastfeeding on mortality in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and cost-evaluation.Eur J Pediatr. 2020 Aug;179(8):1213-1225. doi: 10.1007/s00431-020-03721-5. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Eur J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32592027
Cited by
-
Health spending, illicit financial flows and tax incentives in Malawi.Malawi Med J. 2014 Dec;26(4):133-7. Malawi Med J. 2014. PMID: 26167264 Free PMC article.
-
An analysis of the potential for achieving the fourth millennium development goal in SSA with domestic resources.Global Health. 2015 Feb 25;11:8. doi: 10.1186/s12992-015-0092-1. Global Health. 2015. PMID: 25885642 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Uptake and Timeliness of Newly Introduced Pneumococcal and Rotavirus Vaccines, and of Measles Vaccine in Rural Malawi: A Population Cohort Study.PLoS One. 2016 May 6;11(5):e0154997. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154997. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27152612 Free PMC article.
-
Illicit financial flows and the provision of child and maternal health services in low- and middle-income countries.BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2020 Jul 11;20(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12914-020-00236-w. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2020. PMID: 32653039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pritchett L, Summers LH, 1996. Wealthier is Healthier. Journal of Human Resources, 31: 841–68.
-
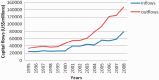
- Boyce JK, Ndikumana L. Capital flight from Sub-Saharan African countries: updated estimates, 1970–2010, Amherst, MA: Political Economy Research Institute, 2012, 2012
-
- unstats|Millennium Indicators. See http://mdgs.un.org/unsd/mdg/host.aspx?Content=indicators/officiallist.htm (last checked 13 November 2013)
-
- Countdown 2015. Building a Future for Women and Children: The 2012 Report. See http://www.countdown2015mnch.org/reports-and-articles/2012-report (last checked 13 November 2013)
-
- Halleröd B, Rothstein B, Daoud A and Nandy S. Bad governance and poor children: a comparative analysis of government efficiency and severe child deprivation in 68 low- and middle-income countries. World Dev 2013;48:19–31. See http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0305750X13000831 (last checked 13 November 2013)
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials