Primary auditory cortical responses to electrical stimulation of the thalamus
- PMID: 24335216
- PMCID: PMC3949229
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00749.2012
Primary auditory cortical responses to electrical stimulation of the thalamus
Abstract
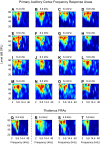
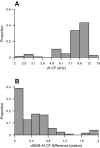
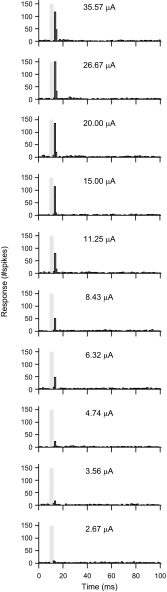
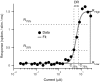
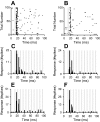
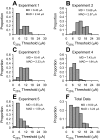
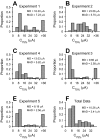
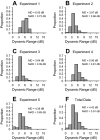
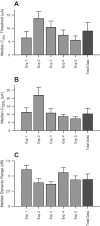
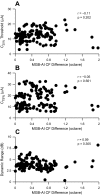
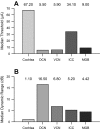
Cochlear implant electrical stimulation of the auditory system to rehabilitate deafness has been remarkably successful. Its deployment requires both an intact auditory nerve and a suitably patent cochlear lumen. When disease renders prerequisite conditions impassable, such as in neurofibromatosis type II and cochlear obliterans, alternative treatment targets are considered. Electrical stimulation of the cochlear nucleus and midbrain in humans has delivered encouraging clinical outcomes, buttressing the promise of central auditory prostheses to mitigate deafness in those who are not candidates for cochlear implantation. In this study we explored another possible implant target: the auditory thalamus. In anesthetized cats, we first presented pure tones to determine frequency preferences of thalamic and cortical sites. We then electrically stimulated tonotopically organized thalamic sites while recording from primary auditory cortical sites using a multichannel recording probe. Cathode-leading biphasic thalamic stimulation thresholds that evoked cortical responses were much lower than published accounts of cochlear and midbrain stimulation. Cortical activation dynamic ranges were similar to those reported for cochlear stimulation, but they were narrower than those found through midbrain stimulation. Our results imply that thalamic stimulation can activate auditory cortex at low electrical current levels and suggest an auditory thalamic implant may be a viable central auditory prosthesis.
Keywords: anodic stimulation; auditory thalamic implant; cathodic stimulation; deafness; medial geniculate body.
Figures
References
-
- Bierer JA, Middlebrooks JC. Auditory cortical images of cochlear-implant stimuli: dependence on electrode configuration. J Neurophysiol 87: 478–492, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Calixto R, Lenarz M, Neuheiser A, Scheper V, Lenarz T, Lim HH. Co-activation of different neurons within an isofrequency lamina of the inferior colliculus elicits enhanced auditory cortical activation. J Neurophysiol 108: 1199–1210, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Cant NB, Benson CG. Multiple topographically organized projections connect the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus to the ventral division of the medial geniculate nucleus in the gerbil, Meriones unguiculatus. J Comp Neurol 503: 432–453, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Cetas JS, Price RO, Crowe J, Velenovsky DS, McMullen NT. Dendritic orientation and laminar architecture in the rabbit auditory thalamus. J Comp Neurol 458: 307–317, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

