Strategies targeting cAMP signaling in the treatment of polycystic kidney disease
- PMID: 24335972
- PMCID: PMC3871779
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013040398
Strategies targeting cAMP signaling in the treatment of polycystic kidney disease
Abstract
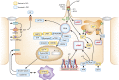
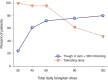
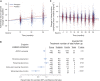
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a leading cause of ESRD worldwide. In PKD, excessive cell proliferation and fluid secretion, pathogenic interactions of mutated epithelial cells with an abnormal extracellular matrix and alternatively activated interstitial macrophages, and the disruption of mechanisms controlling tubular diameter contribute to cyst formation. Studies with animal models suggest that several diverse pathophysiologic mechanisms, including dysregulation of intracellular calcium levels and cAMP signaling, mediate these cystogenic mechanisms. This article reviews the evidence implicating calcium and cAMP as central players in a network of signaling pathways underlying the pathogenesis of PKD and considers the therapeutic relevance of treatment strategies targeting cAMP signaling.
Figures
References
-
- Nauli SM, Alenghat FJ, Luo Y, Williams E, Vassilev P, Li X, Elia AEH, Lu W, Brown EM, Quinn SJ, Ingber DE, Zhou J: Polycystins 1 and 2 mediate mechanosensation in the primary cilium of kidney cells. Nat Genet 33: 129–137, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Nauli SM, Rossetti S, Kolb RJ, Alenghat FJ, Consugar MB, Harris PC, Ingber DE, Loghman-Adham M, Zhou J: Loss of polycystin-1 in human cyst-lining epithelia leads to ciliary dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 1015–1025, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

