miR-16 and miR-26a target checkpoint kinases Wee1 and Chk1 in response to p53 activation by genotoxic stress
- PMID: 24336073
- PMCID: PMC3877554
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.483
miR-16 and miR-26a target checkpoint kinases Wee1 and Chk1 in response to p53 activation by genotoxic stress
Abstract
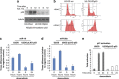
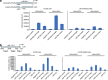
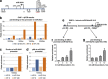
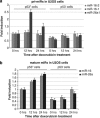
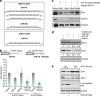
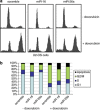
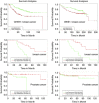
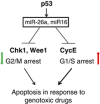
The tumour suppressor p53 is a crucial regulator of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by acting as a transcription factor to regulate a variety of genes. At least in part, this control is exerted by p53 via regulating expression of numerous microRNAs. We identified two abundantly expressed microRNAs, miR-16 and miR-26a, whose expression is regulated by p53 during the checkpoint arrest induced by the genotoxic drug, doxorubicin. Importantly, among the targets of these miRs are two critical checkpoint kinases, Chk1 and Wee1. The p53-dependent augmentation of miR-16 and miR-26a expression levels led to the cell cycle arrest of tumour cells in G1/S and increased apoptosis. Strikingly, the bioinformatics analysis of survival times for patients with breast and prostate cancers has revealed that co-expression of mir-16 and miR-26a correlated with a better survival outcome. Collectively, our data provide a novel mechanism whereby p53 represses Chk1 and Wee1 expression, at least partially, via upregulation of miR-16 and miR-26a and thus sensitizes tumour cells to genotoxic therapies.
Figures
References
-
- Bourdon JC, De Laurenzi V, Melino G, Lane D. p53: 25 years of research and more questions to answer. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10:397–399. - PubMed
-
- Brown JP, Wei WY, Sedivy JM. Bypass of senescence after disruption of p21(CIP1/WAF1) gene in normal diploid human fibroblasts. Science. 1997;277:831–834. - PubMed
-
- Deng C, Zhang P, Harper JW, Elledge SJ, Leder P. Mice lacking p21CIP1/WAF1 undergo normal development, but are defective in G1 checkpoint control. Cell. 1995;82:675–684. - PubMed
-
- Waldman T, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. P21 is necessary for the P53-mediated G(1) arrest in human cancer-cells. Cancer Res. 1995;55:5187–5190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

