Human memory T cells: generation, compartmentalization and homeostasis
- PMID: 24336101
- PMCID: PMC4032067
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3567
Human memory T cells: generation, compartmentalization and homeostasis
Abstract
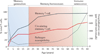
Memory T cells constitute the most abundant lymphocyte population in the body for the majority of a person's lifetime; however, our understanding of memory T cell generation, function and maintenance mainly derives from mouse studies, which cannot recapitulate the exposure to multiple pathogens that occurs over many decades in humans. In this Review, we discuss studies focused on human memory T cells that reveal key properties of these cells, including subset heterogeneity and diverse tissue residence in multiple mucosal and lymphoid tissue sites. We also review how the function and the adaptability of human memory T cells depend on spatial and temporal compartmentalization.
Figures


References
-
- Remakus S, Sigal LJ. Memory CD8(+) T cell protection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;785:77–86. - PubMed
-
- Teijaro JR, et al. Costimulation modulation uncouples protection from immunopathology in memory T cell responses to influenza virus. J Immunol. 2009;182:6834–6843. - PubMed
-
-
Teijaro JR, et al. Cutting edge: tissue-retentive lung memory CD4 T cells mediate optimal protection to respiratory virus infection. J Immunol. 2011;187:5510–5514. This study identified retention of CD4+ TRM cells in mouse lungs and demonstrated superior protective capacity of lung TRM cells compared with circulating spleen memory CD4+ T cells to influenza virus infection.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

