Age at surgical menopause influences cognitive decline and Alzheimer pathology in older women
- PMID: 24336141
- PMCID: PMC3902759
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000033
Age at surgical menopause influences cognitive decline and Alzheimer pathology in older women
Abstract
Objective: To determine the association between age at surgical menopause and both cognitive decline and Alzheimer disease (AD) pathology in 2 longitudinal cohorts.
Methods: Female subjects from 2 longitudinal studies of cognitive decline (Religious Orders Study and Rush Memory and Aging Project) were included (total n = 1,884). The primary analysis examined the association between age at surgical menopause and decline in a global cognition score. Secondary analyses examined additional outcomes: 1) decline in 5 cognitive subdomains and 2) a global measure of the burden of AD pathology. In exploratory analyses, we examined the effect of hormone replacement therapy (HRT). We adjusted all models for age, education, smoking, and cohort and stratified by surgical vs natural menopause.
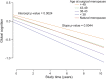
Results: For the 32% of subjects with surgical menopause, earlier age at menopause was associated with faster decline in global cognition (p = 0.0007), specifically episodic memory (p = 0.0003) and semantic memory (p = 0.002). Earlier age at menopause was also associated with increased AD neuropathology (p = 0.038), in particular neuritic plaques (p = 0.013). HRT use for at least 10 years, when administered within a 5-year perimenopausal window, was associated with decreased decline in global cognition. No associations were seen in women who had natural menopause.
Conclusions: Early age at surgical menopause was associated with cognitive decline and AD neuropathology. Ongoing studies should clarify the potential effect of HRT on this relationship.
Figures
Comment in
-
Is there a link between gynecologic surgeries and Alzheimer disease?Neurology. 2014 Jan 21;82(3):196-7. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000043. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24336139 No abstract available.
References
-
- Boulware MI, Kent BA, Frick KM. The impact of age-related ovarian hormone loss on cognitive and neural function. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 2012;10:165–184 - PubMed
-
- Coppus AM, Evenhuis HM, Verberne GJ, et al. Early age at menopause is associated with increased risk of dementia and mortality in women with Down syndrome. J Alzheimers Dis 2010;19:545–550 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG17917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K25 AG041906/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG10161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32AI074549/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG034290/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022018/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG30146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS059873/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG15819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
